Neuroprotective Potency of Neolignans in Magnolia officinalis Cortex Against Brain Disorders
- PMID: 35784755
- PMCID: PMC9244706
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.857449
Neuroprotective Potency of Neolignans in Magnolia officinalis Cortex Against Brain Disorders
Abstract
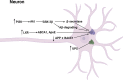
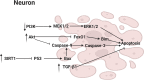
In recent years, neurological diseases including Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease and stroke are one of the main causes of death in the world. At the same time, the incidence of psychiatric disorders including depression and anxiety has been increasing. Accumulating elderly and stressed people suffer from these brain disorders, which is undoubtedly a huge burden on the modern aging society. Neolignans, the main active ingredients in Magnolia officinalis cortex, were reported to have neuroprotective effects. In addition, the key bioactive ingredients of neolignans, magnolol (1) and honokiol (2), were proved to prevent and treat neurological diseases and psychiatric disorders by protecting nerve cells and brain microvascular endothelial cells (BMECs). Furthermore, neolignans played a role in protecting nerve cells via regulation of neuronal function, suppression of neurotoxicity, etc. This review summarizes the neuroprotective effect, primary mechanisms of the leading neolignans and provides new prospects for the treatment of brain disorders in the future.
Keywords: Magnolia officinalis; brain disorders; multiple pathways; neolignans; neuroprotective effect.
Copyright © 2022 Zhu, Liu, Zhang, Xiong, Zhang, Hao and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
HSY was employed by Pharmaceutical Group Co., LTD. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Antidepressant-like effects of the mixture of honokiol and magnolol from the barks of Magnolia officinalis in stressed rodents.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2008 Apr 1;32(3):715-25. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2007.11.020. Epub 2007 Nov 28. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2008. PMID: 18093712
-
A honokiol-enriched Magnolia officinalis Rehder & E.H. Wilson. bark extract possesses anxiolytic-like activity with neuroprotective effect through the modulation of CB1 receptor.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2021 Aug 12;73(9):1161-1168. doi: 10.1093/jpp/rgab067. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33950239
-
The rich pharmacological activities of Magnolia officinalis and secondary effects based on significant intestinal contributions.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Dec 5;281:114524. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114524. Epub 2021 Aug 13. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34400262
-
Magnolol and honokiol from Magnolia officinalis enhanced antiviral immune responses against grass carp reovirus in Ctenopharyngodon idella kidney cells.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017 Apr;63:245-254. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2017.02.020. Epub 2017 Feb 20. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28232195
-
Safety and Toxicology of Magnolol and Honokiol.Planta Med. 2018 Nov;84(16):1151-1164. doi: 10.1055/a-0642-1966. Epub 2018 Jun 20. Planta Med. 2018. PMID: 29925102 Review.
Cited by
-
Neuropharmacological potential of honokiol and its derivatives from Chinese herb Magnolia species: understandings from therapeutic viewpoint.Chin Med. 2023 Nov 24;18(1):154. doi: 10.1186/s13020-023-00846-1. Chin Med. 2023. PMID: 38001538 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Soluble individual metal atoms and ultrasmall clusters catalyze key synthetic steps of a natural product synthesis.Commun Chem. 2024 Apr 4;7(1):76. doi: 10.1038/s42004-024-01160-z. Commun Chem. 2024. PMID: 38575790 Free PMC article.
-
Extraction and Biological Activity of Lignanoids from Magnolia officinalis Rehder & E.H.Wilson Residual Waste Biomass Using Deep Eutectic Solvents.Molecules. 2024 May 16;29(10):2352. doi: 10.3390/molecules29102352. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38792212 Free PMC article.
-
Brain and serum metabolomic studies reveal therapeutic effects of san hua decoction in rats with ischemic stroke.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Nov 30;14:1289558. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1289558. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 38098862 Free PMC article.
-
Research Progress on Natural Plant Molecules in Regulating the Blood-Brain Barrier in Alzheimer's Disease.Molecules. 2023 Nov 16;28(22):7631. doi: 10.3390/molecules28227631. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 38005352 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

