An Efficient UPLC-MS/MS Method Established to Detect Relugolix Concentration in Rat Plasma
- PMID: 35784757
- PMCID: PMC9243301
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.874973
An Efficient UPLC-MS/MS Method Established to Detect Relugolix Concentration in Rat Plasma
Abstract
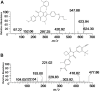
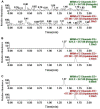
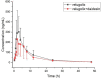
Relugolix, a gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) receptor antagonist, has been well studied in the treatment of endometriosis symptomatic. It is mainly metabolized by the CYP3A subfamily of P450 enzymes, while minorly metabolized by CYP2C8. Daidzein in different dose groups exhibited a certain induction on the mRNA expression level of CYP3A4 and resulted in the potent induction of CYP3A4. However, it is still unknown whether daidzein and relugolix interact. We developed an effective ultra-performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS) method to study the effect of daidzein on the pharmacokinetics of relugolix in rats after oral administration of 12 mg/kg relugolix in a single or mixed of 50 mg/kg daidzein. The results showed that the method had respectable linearity (r 2 > 0.999) on the scale of 0.7-1000 ng/mL. The intra-day precision was between 3.0% and 8.4% in this assay, and the inter-day was between 4.0% and 11.7%. The intra-day accuracy was from -4.3% to 6.1%, and the inter-day was 2.9% to 12.1%. Another three key indicators, including the stability, the recovery rate of extraction and the new technique's matrix effect, were perfectly in accord with the test verification rule in the biological medium by the United States Food and Drug Administration. Meanwhile, treatment with daidzein led to a decrease in Cmax and AUC0-t of relugolix by about 15.56% and 21.36%, respectively. Although there was no statistical difference in pharmacokinetic parameters, it reflected the induction trend of daidzein on relugolix metabolism for food-drug interaction. It would provide reference and improvement value for subsequent experiments.
Keywords: GnRH antagonist; daidzein; endometriosis; relugolix; uterine fibroids.
Copyright © 2022 Xing, Liu, Yao, Wang, Xie, Luo, Luo and Tang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[UPLC-MS/MS determination of tanshinone ⅡA, salvianolic acid B and ginsenoside Rg₁ in Fufang Danshen preparation in rat plasma and brain tissues].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2017 Feb;42(3):580-586. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.2017.0014. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 28952268 Chinese.
-
Transfer of the Oral Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone Receptor Antagonist Relugolix Into Breast Milk of Healthy Lactating Women.Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2025 Feb;13(1):e70067. doi: 10.1002/prp2.70067. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2025. PMID: 39887952 Free PMC article.
-
Relugolix, an oral gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor antagonist, reduces endometriosis-associated pain in a dose-response manner: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study.Fertil Steril. 2021 Feb;115(2):397-405. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2020.07.055. Epub 2020 Sep 7. Fertil Steril. 2021. PMID: 32912633 Clinical Trial.
-
Relugolix for the treatment of uterine fibroids.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2020 Oct;21(14):1667-1674. doi: 10.1080/14656566.2020.1787988. Epub 2020 Jul 17. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 32674616 Review.
-
An Expert Review on the Combination of Relugolix With Definitive Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2022 Jun 1;113(2):278-289. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2021.12.005. Epub 2021 Dec 17. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2022. PMID: 34923058 Review.
Cited by
-
Relugolix in Combination with Androgen Receptor Pathway Inhibitors in the Treatment of Metastatic Prostate Cancer: A Clinical Perspective.Target Oncol. 2025 Jul;20(4):627-635. doi: 10.1007/s11523-025-01150-8. Epub 2025 May 16. Target Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40377869 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chaichian S., Kabir A., Mehdizadehkashi A., Rahmani K., Moghimi M., Moazzami B. (2017). Comparing the Efficacy of Surgery and Medical Therapy for Pain Management in Endometriosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pain Physician 20, 185–195. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

