Intracapsular Femoral Neck Fractures in the Elderly
- PMID: 35785116
- PMCID: PMC9246523
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0041-1736473
Intracapsular Femoral Neck Fractures in the Elderly
Abstract
Currently, intracapsular femoral neck fracture (IFNF) is still a great challenge for orthopedists. In spite of the progress that has been made, a high mortality rate persists in the first year, especially in Brazil, where there is no awareness that such fractures in elderly patients should be treated as a medical emergency. The present article seeks to provide an update on the preoperative, surgical, and postoperative approaches.
Keywords: elderly; femoral neck fractures; hip fractures.
Sociedade Brasileira de Ortopedia e Traumatologia. This is an open access article published by Thieme under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonDerivative-NonCommercial License, permitting copying and reproduction so long as the original work is given appropriate credit. Contents may not be used for commecial purposes, or adapted, remixed, transformed or built upon. ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ ).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflito de Interesses Os autores declaram não haver conflito de interesses.
Figures
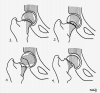
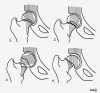
References
-
- The Study of Osteoporotic Fractures Research Group Cummings S R, Black D M, Nevitt M C.Bone density at various sites for prediction of hip fractures Lancet 1993341(8837):72–75. - PubMed
-
- Li M, Cole P A. Anatomical considerations in adult femoral neck fractures: how anatomy influences the treatment issues? Injury. 2015;46(03):453–458. - PubMed
-
- Garden R S. Low-Angle Fixation In Fractures Of The Femoral Neck. The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. British volume. 1961;43-B(04):647–663.
-
- Foex B A, Russell A. BET 2: CT versus MRI for occult hip fractures. Emerg Med J. 2018;35(10):645–647. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

