Results of an Innovative Program for Surveillance, Prophylaxis, and Treatment of Infectious Complications Following Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation in Hematological Malignancies (BATMO Protocol)
- PMID: 35785189
- PMCID: PMC9247274
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.874117
Results of an Innovative Program for Surveillance, Prophylaxis, and Treatment of Infectious Complications Following Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation in Hematological Malignancies (BATMO Protocol)
Abstract
Background: Infectious complications are a significant cause of morbidity and mortality in patients undergoing allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation (Allo-SCT). The BATMO (Best-Antimicrobial-Therapy-TMO) is an innovative program for infection prevention and management and has been used in our centre since 2019. The specific features of the BATMO protocol regard both prophylaxis during neutropenia (abandonment of fluoroquinolone, posaconazole use in high-risk patients, aerosolized liposomal amphotericin B use until engraftment or a need for antifungal treatment, and letermovir use in CMV-positive recipients from day 0 to day +100) and therapy (empirical antibiotics based on patient clinical history and colonization, new antibiotics used in second-line according to antibiogram with the exception of carbapenemase-producing K pneumoniae for which the use in first-line therapy is chosen).
Methods: Data on the infectious complications of 116 transplant patients before BATMO protocol (Cohort A; 2016 - 2018) were compared to those of 84 transplant patients following the introduction of the BATMO protocol (Cohort B; 2019 - 2021). The clinical and transplant characteristics of the 2 Cohorts were comparable, even though patients in Cohort B were at a higher risk of developing bacterial, fungal, and CMV infections, due to a significantly higher proportion of myeloablative regimens and haploidentical donors.
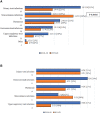
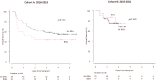
Results: No change in the incidence of infections with organ localization was observed between the two Cohorts. A significant reduction in Clostridioides difficile infections by day +100 was observed in Cohort B (47% vs. 15%; p=0.04). At day +30, a higher incidence of Gram-negative bloodstream infections (BSIs) was observed in Cohort B (12% vs. 23%; p=0.05). By day +100 and between days +100 and +180, the incidence of BSIs and of the various etiological agents, the mortality from Gram-negative bacteria, and the incidence of invasive fungal infections were not different in the two Cohorts. The incidence of CMV reactivations by day +100 dropped drastically in patients of Cohort B, following letermovir registration (51% vs. 15%; p=0.00001).
Discussion: The results of this study suggest that the BATMO program is safe. In particular, the choice to avoid prophylaxis with fluoroquinolone was associated with an increase in Gram-negative BSIs by day +30, but this did not translate into higher levels of mortality. Moreover, this strategy was associated with a significant reduction of Clostridiodes difficile infections. The efficacy of anti-CMV prophylaxis with letermovir was confirmed by a significant reduction in CMV reactivations. Even though patients in Cohort B were at higher risk of developing fungal infections (more haploidentical transplants with more myeloablative regimens), the extensive use of posaconazole for prophylaxis balanced this risk, and no increase in the incidence of fungal-associated complications was observed.
Keywords: bacterial infections; fungal infections; multi-drug resistance; prophylaxis; viral infections.
Copyright © 2022 Malagola, Turra, Signorini, Corbellini, Polverelli, Masina, Del Fabro, Lorenzotti, Fumarola, Farina, Morello, Radici, Buttini, Colnaghi, Bernardi, Re, Caruso, Castelli and Russo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Styczyński J, Tridello G, Koster L, Iacobelli S, van Biezen A, van der Werf S, et al. . Death After Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: Changes Over Calendar Year Time, Infections and Associated Factors. Bone Marrow Transplant (2020) 55(1):126–36. doi: 10.1038/s41409-019-0624-z - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Girmenia C, Bertaina A, Piciocchi A, Perruccio K, Algarotti A, Busca A, et al. . Incidence, Risk Factors and Outcome of Pre-Engraftment Gram-Negative Bacteremia After Allogeneic and Autologous Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: An Italian Prospective Multicenter Survey. Clin Infect Dis (2017) 65(11):1884–96. doi: 10.1093/cid/cix690 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Maertens JA, Girmenia C, Brüggemann RJ, Duarte RF, Kibbler CC, Ljungman P, et al. . European Guidelines for Primary Antifungal Prophylaxis in Adult Haematology Patients: Summary of the Updated Recommendations From the European Conference on Infections in Leukaemia. J Antimicrob Chemother (2018) 73(12):3221–30. doi: 10.1093/jac/dky286 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

