High-resolution 3D demonstration of regional heterogeneity in the glymphatic system
- PMID: 35786032
- PMCID: PMC9580176
- DOI: 10.1177/0271678X221109997
High-resolution 3D demonstration of regional heterogeneity in the glymphatic system
Abstract
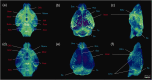
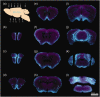
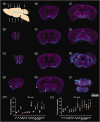
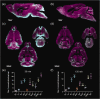
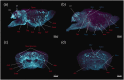
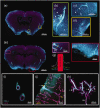
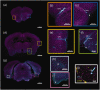
Accumulating evidence indicates that the glymphatic system has a critical role in maintaining brain homeostasis. However, the detailed anatomy of the glymphatic pathway is not well understood, mostly due to a lack of high spatial resolution 3D visualization. In this study, a fluorescence micro-optical sectioning tomography (fMOST) was used to characterize the glymphatic architecture in the mouse brain. At 30 and 120 min after intracisternal infusion with fluorescent dextran (Dex-3), lectin was injected to stain the cerebral vasculature. Using fMOST, a high-resolution 3D dataset of the brain-wide distribution of Dex-3 was acquired. Combined with fluorescence microscopy and microplate array, the heterogeneous glymphatic flow and the preferential irrigated regions were identified. These cerebral regions containing large-caliber penetrating arteries and/or adjacent to the subarachnoid space had more robust CSF flow compared to other regions. Moreover, the major glymphatic vessels for CSF influx and fluid efflux in the entire brain were shown in 3D. This study demonstrates the regional heterogeneity in the glymphatic system and provides an anatomical resource for further investigation of the glymphatic function.
Keywords: Glymphatic system; cerebrospinal fluid; fluorescence micro-optical sectioning tomography; paravascular spaces; vasculature.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Characterizing the glymphatic influx by utilizing intracisternal infusion of fluorescently conjugated cadaverine.Life Sci. 2018 May 15;201:150-160. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2018.03.057. Epub 2018 Mar 30. Life Sci. 2018. PMID: 29605446
-
Paravascular channels, cisterns, and the subarachnoid space in the rat brain: A single compartment with preferential pathways.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2017 Apr;37(4):1374-1385. doi: 10.1177/0271678X16655550. Epub 2016 Jan 1. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2017. PMID: 27306753 Free PMC article.
-
Intracranial pressure elevation alters CSF clearance pathways.Fluids Barriers CNS. 2020 Apr 16;17(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s12987-020-00189-1. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2020. PMID: 32299464 Free PMC article.
-
Paravascular spaces: entry to or exit from the brain?Exp Physiol. 2019 Jul;104(7):1013-1017. doi: 10.1113/EP087424. Epub 2019 Jan 9. Exp Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30582766 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Glymphatic System and Subarachnoid Lymphatic-Like Membrane: Recent Developments in Cerebrospinal Fluid Research.World Neurosurg. 2024 Oct;190:147-156. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2024.07.062. Epub 2024 Jul 11. World Neurosurg. 2024. PMID: 39002777 Review.
Cited by
-
Reimagining the meninges from a neuroimmune perspective: a boundary, but not peripheral.J Neuroinflammation. 2024 Nov 15;21(1):299. doi: 10.1186/s12974-024-03286-2. J Neuroinflammation. 2024. PMID: 39548515 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional aspects of the brain lymphatic drainage system in aging and neurodegenerative diseases.J Biomed Res. 2024 Mar 2;38(3):206-221. doi: 10.7555/JBR.37.20230264. J Biomed Res. 2024. PMID: 38430054 Free PMC article.
-
NIR-II nanoprobes for investigating the glymphatic system function under anesthesia and stroke injury.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 Apr 23;22(1):200. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02481-w. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 38654299 Free PMC article.
-
Meningeal lymphatic drainage: novel insights into central nervous system disease.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025 May 5;10(1):142. doi: 10.1038/s41392-025-02177-z. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025. PMID: 40320416 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Whole-brain Optical Imaging: A Powerful Tool for Precise Brain Mapping at the Mesoscopic Level.Neurosci Bull. 2023 Dec;39(12):1840-1858. doi: 10.1007/s12264-023-01112-y. Epub 2023 Sep 16. Neurosci Bull. 2023. PMID: 37715920 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

