Going beyond the spacing effect: Does it matter how time on a task is distributed?
- PMID: 35786148
- PMCID: PMC10119902
- DOI: 10.1177/17470218221113933
Going beyond the spacing effect: Does it matter how time on a task is distributed?
Abstract
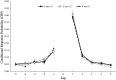
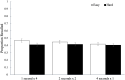
We assessed the effects of removing some constraints that characterise traditional experiments on the effects of spaced, rather than massed, study opportunities. In five experiments-using lists of to-be-remembered words-we examined the effects of how total study time was distributed across multiple repetitions of a given to-be-remembered word. Overall, within a given list, recall profited from study time being distributed (e.g., four 1-s presentations or two 2-s presentations vs one 4-s presentation). Among the implications of these findings is that if students choose to engage in massed studying (by virtue of constraints on their study time or a failure to appreciate the benefits of spaced study sessions), then studying the information twice but for half the time may produce memory benefits in a single study session.
Keywords: Spacing effect; difficulty; free recall; repetition effect.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures












Similar articles
-
Electrophysiological correlates of word repetition spacing: ERP and induced band power old/new effects with massed and spaced repetitions.Int J Psychophysiol. 2007 Dec;66(3):205-14. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2007.07.003. Epub 2007 Jul 14. Int J Psychophysiol. 2007. PMID: 17688964
-
Within-session spacing improves delayed recall in children.Memory. 2015;23(4):625-32. doi: 10.1080/09658211.2014.915975. Epub 2014 May 7. Memory. 2015. PMID: 24805305
-
Spacing of repetitions improves learning and memory after moderate and severe TBI.J Clin Exp Neuropsychol. 2003 Feb;25(1):49-58. doi: 10.1076/jcen.25.1.49.13631. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol. 2003. PMID: 12607171
-
The role of reminding in the effects of spaced repetitions on cued recall: sufficient but not necessary.J Exp Psychol Learn Mem Cogn. 2014 Jan;40(1):94-105. doi: 10.1037/a0034055. Epub 2013 Aug 12. J Exp Psychol Learn Mem Cogn. 2014. PMID: 23937236 Free PMC article.
-
Distributed practice in verbal recall tasks: A review and quantitative synthesis.Psychol Bull. 2006 May;132(3):354-80. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.132.3.354. Psychol Bull. 2006. PMID: 16719566 Review.
Cited by
-
Counting days is a spacing incentive that unlocks the potential of low GPA students.NPJ Sci Learn. 2025 Jun 5;10(1):35. doi: 10.1038/s41539-025-00322-5. NPJ Sci Learn. 2025. PMID: 40473676 Free PMC article.
-
Re-examining the testing effect as a learning strategy: the advantage of retrieval practice over concept mapping as a methodological artifact.Front Psychol. 2023 Dec 21;14:1258359. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1258359. eCollection 2023. Front Psychol. 2023. PMID: 38213612 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Appleton-Knapp S., Bjork R. A., Wickens T. D. (2005). Examining the spacing effect in advertising: Encoding variability, retrieval processes and their interaction. Journal of Consumer Research, 32(2), 266–276. 10.1086/432236 - DOI
-
- Balota D. A., Duchek J. M., Logan J. M. (2007. a). Is expanded retrieval practice a superior form of spaced retrieval? A critical review of the extant literature. In Nairne J. S. (Ed.), The foundations of remembering: Essays in honor of Henry L. Roediger, III (pp. 83–105). Psychology Press. 10.4324/9780203837672 - DOI

