Assessing and validating reliable change across ADNI protocols
- PMID: 35786312
- PMCID: PMC9308719
- DOI: 10.1080/13803395.2022.2082386
Assessing and validating reliable change across ADNI protocols
Abstract
Objective: Reliable change methods can aid in determining whether changes in cognitive performance over time are meaningful. The current study sought to develop and cross-validate 12-month standardized regression-based (SRB) equations for the neuropsychological measures commonly administered in the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) longitudinal study.
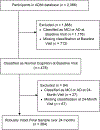
Method: Prediction algorithms were developed using baseline score, retest interval, the presence/absence of a 6-month evaluation, age, education, sex, and ethnicity in two different samples (n = 192 each) of robustly cognitively intact community-dwelling older adults from ADNI - matched for demographic and testing factors. The developed formulae for each sample were then applied to one of the samples to determine goodness-of-fit and appropriateness of combining samples for a single set of SRB equations.
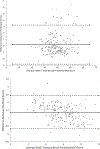
Results: Minimal differences were seen between Observed 12-month and Predicted 12-month scores on most neuropsychological tests from ADNI, and when compared across samples the resultant Predicted 12-month scores were highly correlated. As a result, samples were combined and SRB prediction equations were successfully developed for each of the measures.
Conclusions: Establishing cross-validation for these SRB prediction equations provides initial support of their use to detect meaningful change in the ADNI sample, and provides the basis for future research with clinical samples to evaluate potential clinical utility. While some caution should be considered for measuring true cognitive change over time - particularly in clinical samples - when using these prediction equations given the relatively lower coefficients of stability observed, use of these SRBs reflects an improvement over current practice in ADNI.
Keywords: ADNI; Reliable change; assessment; memory; neuropsychology; practice effects.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Validation of one-week reliable change methods in cognitively intact community-dwelling older adults.Neuropsychol Dev Cogn B Aging Neuropsychol Cogn. 2021 May;28(3):472-492. doi: 10.1080/13825585.2020.1787942. Epub 2020 Jul 2. Neuropsychol Dev Cogn B Aging Neuropsychol Cogn. 2021. PMID: 32613913 Free PMC article.
-
Generalizability of reliable change equations for the RBANS over one year in community-dwelling older adults.J Clin Exp Neuropsychol. 2020 May;42(4):394-405. doi: 10.1080/13803395.2020.1740654. Epub 2020 Mar 26. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol. 2020. PMID: 32212958
-
Validating 1-Year Reliable Change Methods.Arch Clin Neuropsychol. 2021 Jan 15;36(1):87-98. doi: 10.1093/arclin/acaa055. Arch Clin Neuropsychol. 2021. PMID: 32885234 Free PMC article.
-
The Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative: a review of papers published since its inception.Alzheimers Dement. 2013 Sep;9(5):e111-94. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2013.05.1769. Epub 2013 Aug 7. Alzheimers Dement. 2013. PMID: 23932184 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative in the era of Alzheimer's disease treatment: A review of ADNI studies from 2021 to 2022.Alzheimers Dement. 2024 Jan;20(1):652-694. doi: 10.1002/alz.13449. Epub 2023 Sep 12. Alzheimers Dement. 2024. PMID: 37698424 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Axonal injury, sleep disturbances, and memory following traumatic brain injury.Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2024 Sep;11(9):2314-2326. doi: 10.1002/acn3.52145. Epub 2024 Jul 19. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39031956 Free PMC article.
-
Machine learning on longitudinal multi-modal data enables the understanding and prognosis of Alzheimer's disease progression.iScience. 2024 Jun 14;27(7):110263. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110263. eCollection 2024 Jul 19. iScience. 2024. PMID: 39040055 Free PMC article.
-
Characterizing and validating 12-month reliable cognitive change in Early-Onset Alzheimer's Disease for use in clinical trials.J Prev Alzheimers Dis. 2025 Apr;12(4):100075. doi: 10.1016/j.tjpad.2025.100075. Epub 2025 Feb 16. J Prev Alzheimers Dis. 2025. PMID: 39956674 Free PMC article.
-
Longitudinal cognitive performance of participants with sporadic early onset Alzheimer's disease from LEADS.Alzheimers Dement. 2025 Feb;21(2):e14439. doi: 10.1002/alz.14439. Epub 2024 Dec 23. Alzheimers Dement. 2025. PMID: 39713873 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ADNI1. (2004). Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative: ADNI Procedures Manual. Retrieved from http://adni.loni.usc.edu/wp-content/uploads/2010/09/ADNI_GeneralProcedur...
-
- ADNI2. (2011). Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative: ADNI2 Procedures Manual. Retrieved from https://adni.loni.usc.edu/wp-content/uploads/2008/07/adni2-procedures-ma... - PubMed
-
- ADNI3. (2016). Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative: ADNI3 Procedures Manual. Retrieved from https://adni.loni.usc.edu/wp-content/uploads/2012/10/ADNI3-Procedures-Ma...
-
- ADNIGO. (2009). Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative: ADNI Grand Opportunities Procedures Manual. Retrieved from http://adni.loni.usc.edu/wp-content/uploads/2008/07/ADNI_GO_Procedures_M...
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
