Financial Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on Endodontic Clinics in Egypt: A Questionnaire-Based Report
- PMID: 35786575
- PMCID: PMC9285999
- DOI: 10.14744/eej.2022.15238
Financial Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on Endodontic Clinics in Egypt: A Questionnaire-Based Report
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the financial impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on endodontic clinics in Egypt.
Methods: Two hundred Egyptian endodontists holding a minimum of a master's degree were invited to participate in an online survey in March 2021. Participants accessed the survey link shared on the social media group of the Egyptian Society of Endodontology. Participants read and signed an electronic informed consent before participating in this study. The questionnaire was designed exclusively by the authors. A draft was pilot tested on a sample of 15 endodontic masters' students at The British University in Egypt. Suggestions and comments to improve clarity, content, and validity were incorporated into the revised survey. The questionnaire was divided into five sections; the first section comprised of questions about the participants' demographic details. The second section targeted the current and future financial impact of COVID-19 on practices. The third section included information about the average patient flow and the introduction of teledentistry in clinical practice. The fourth section assessed the effect of COVID-19 on the staff in the dental clinics and the changes made in response to COVID-19. The last section estimated COVID-19 prevalence among endodontists and staff. Categorical data were presented as frequencies (n) and percentages (%) and were analysed using Fisher's exact test. Quantitative data were presented as mean and standard deviation values. P-values were adjusted for multiple comparisons utilising Bonferroni correction.
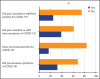
Results: A total of 141 endodontists participated in the survey. The negative financial impact of COVID-19 was reported by 84.39% of the participants. Seventy-eight endodontists (55.3%) suffered from the increased cost of endodontic materials. Of the endodontist respondents, 90.8% suffered from the increased cost of PPE, 82.3% did not charge their patients more, and only 14.4% planned to charge more. A decrease in the number of referred cases for endodontic treatment has been noticed by 58.9%. About 47.5% noticed increased patient phone calls replacing patient visits. Only 12.8% have dismissed staff because of financial problems.
Conclusion: COVID-19 has negatively affected most endodontists financially and significantly affected their practices' strategies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors deny any conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Endodontic treatment during the COVID-19 pandemic - perception and behaviour of dental professionals.Acta Odontol Latinoam. 2021 Apr 1;34(1):63-70. doi: 10.54589/aol.34/1/063. Acta Odontol Latinoam. 2021. PMID: 34137780 English.
-
Differences in endodontic emergency management by endodontists and general dental practitioners in COVID-19 times.Braz Oral Res. 2020 Oct 30;34:e122. doi: 10.1590/1807-3107bor-2020.vol34.0122. eCollection 2020. Braz Oral Res. 2020. PMID: 33146318
-
A Cross-sectional Survey on the Impact of Coronavirus Disease 2019 on the Clinical Practice of Endodontists across the United States.J Endod. 2021 Jan;47(1):28-38. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2020.10.002. Epub 2020 Oct 12. J Endod. 2021. PMID: 33058936 Free PMC article.
-
Online medical education in Egypt during the COVID-19 pandemic: a nationwide assessment of medical students' usage and perceptions.BMC Med Educ. 2022 Mar 30;22(1):218. doi: 10.1186/s12909-022-03249-2. BMC Med Educ. 2022. PMID: 35354406 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recommendations for Managing Endodontic Emergencies during Coronavirus Disease 2019 Outbreak.J Endod. 2021 Jan;47(1):3-10. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2020.09.018. Epub 2020 Oct 9. J Endod. 2021. PMID: 33045270 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of the Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic on Dental Visits in Japan.Oral Health Prev Dent. 2023 May 17;21:179-184. doi: 10.3290/j.ohpd.b4100953. Oral Health Prev Dent. 2023. PMID: 37195334 Free PMC article.
-
Teledentistry from research to practice: a tale of nineteen countries.Front Oral Health. 2023 Jun 16;4:1188557. doi: 10.3389/froh.2023.1188557. eCollection 2023. Front Oral Health. 2023. PMID: 37397348 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Impact of COVID-19 on Dental Anesthesiologists: An Online Survey of Board-Certified Dental Anesthesiology Specialists of the Japanese Dental Society of Anesthesiology.Anesth Prog. 2023 Dec 1;70(4):168-172. doi: 10.2344/930714. Anesth Prog. 2023. PMID: 38221698 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) Available at: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019 Accessed Feb 18 2022.
-
- Al Arabiya English Coronavirus: Egypt to lift lockdown from June 27 as COVID-19 restrictions ease. Available at: https://english.alarabiya.net/coronavirus/2020/06/23/Coronavirus-Egypt-t... Accessed Dec 13 2021.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

