High-Dose Dual Therapy Versus Bismuth-Containing Quadruple Therapy for the Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 35786612
- PMCID: PMC9317580
- DOI: 10.5152/tjg.2022.21579
High-Dose Dual Therapy Versus Bismuth-Containing Quadruple Therapy for the Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of high-dose dual therapy for Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) eradication compared to bismuth-containing quadruple therapy.
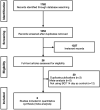
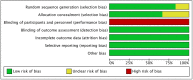
Methods: The electronic database of PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library were searched from inception to March 18, 2021. Randomized, controlled trials that evaluated high-dose dual therapy versus bismuth-containing quadruple therapy for H. pylori infection were included.
Results: We included 6 studies containing 1677 patients with H. pylori infection. This meta-analysis demonstrated that high-dose dual therapy achieved similar eradication rate compared with bismuth-containing quadruple therapy (intention-to-treat: 84.6% vs 83.7%, relative risk (RR) = 1.01, 95% CI: 0.97-1.06, P = .49; per-protocol = 88.4% vs 89.0%, RR = 1.00, 95% CI: 0.97-1.04, P = .99). However, highdose dual therapy showed fewer side effects (13.1% vs 32.0%, RR = 0.51, 95% CI: 0.34-0.78, P = .002) and better compliance (96.1% vs 93.3%, RR = 1.03, 95% CI: 1.00-1.05, P = .03) compared to bismuth-containing quadruple therapy.
Conclusion: This meta-analysis demonstrated that high-dose dual therapy is equally effective with bismuth-containing quadruple therapy in eradicating H. pylori, with fewer side effects and better compliance.
Figures

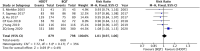

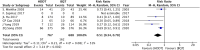


Similar articles
-
High-dose dual therapy versus bismuth-containing quadruple therapy for the treatment of helicobacter pylori infection: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2023 Mar-Apr;29(2):88-94. doi: 10.4103/sjg.sjg_532_22. Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 36960527 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of high-dose dual therapy with bismuth-containing quadruple therapy in Helicobacter pylori-infected treatment-naive patients: An open-label, multicenter, randomized controlled trial.Pharmacotherapy. 2022 Mar;42(3):224-232. doi: 10.1002/phar.2662. Epub 2022 Feb 5. Pharmacotherapy. 2022. PMID: 35075679 Clinical Trial.
-
High dose dual therapy versus bismuth quadruple therapy for Helicobacter pylori eradication treatment: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Feb;98(7):e14396. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000014396. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 30762742 Free PMC article.
-
Eradication Efficacy of Modified Dual Therapy Compared with Bismuth-Containing Quadruple Therapy as a First-Line Treatment of Helicobacter pylori.Am J Gastroenterol. 2019 Mar;114(3):437-445. doi: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000000132. Am J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 30807294 Clinical Trial.
-
Second-line rescue treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection: Where are we now?World J Gastroenterol. 2018 Oct 28;24(40):4548-4553. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i40.4548. World J Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 30386104 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
High-dose dual therapy versus bismuth-containing quadruple therapy for Helicobacter pylori eradication: a systematic review and meta-analysis with trial sequential analysis.Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2023 Jan 10;16:17562848221147756. doi: 10.1177/17562848221147756. eCollection 2023. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 36644129 Free PMC article.
-
Susceptibility-guided sequential strategy versus empirical therapy for Helicobacter pylori infection: study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.Trials. 2023 Jun 19;24(1):413. doi: 10.1186/s13063-023-07457-z. Trials. 2023. PMID: 37337241 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Efficacy of Azithromycin and Clarithromycin in the Management of Helicobacter pylori Infection.Cureus. 2024 Oct 21;16(10):e72033. doi: 10.7759/cureus.72033. eCollection 2024 Oct. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39569309 Free PMC article.
-
Vonoprazan and amoxicillin dual therapy versus bismuth-based therapy for Helicobacter pylori eradication: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent). 2025 Apr 22;38(5):716-721. doi: 10.1080/08998280.2025.2491964. eCollection 2025. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent). 2025. PMID: 40821497 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of vonoprazan-amoxicillin dual therapy for Helicobacter pylori first-line treatment: a single-center, randomized, controlled trial.Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2023 Aug 30;16:17562848231190976. doi: 10.1177/17562848231190976. eCollection 2023. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 37664169 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
