GDF11 inhibits abnormal adipogenesis of condylar chondrocytes in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis
- PMID: 35787089
- PMCID: PMC9350697
- DOI: 10.1302/2046-3758.117.BJR-2022-0019.R1
GDF11 inhibits abnormal adipogenesis of condylar chondrocytes in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis
Abstract
Aims: Abnormal lipid metabolism is involved in the development of osteoarthritis (OA). Growth differentiation factor 11 (GDF11) is crucial in inhibiting the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into adipocytes. However, whether GDF11 participates in the abnormal adipogenesis of chondrocytes in OA cartilage is still unclear.
Methods: Six-week-old female mice were subjected to unilateral anterior crossbite (UAC) to induce OA in the temporomandibular joint (TMJ). Histochemical staining, immunohistochemical staining (IHC), and quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) were performed. Primary condylar chondrocytes of rats were stimulated with fluid flow shear stress (FFSS) and collected for oil red staining, immunofluorescence staining, qRT-PCR, and immunoprecipitation analysis.
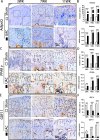
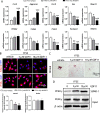
Results: Abnormal adipogenesis, characterized by increased expression of CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein α (CEBPα), fatty acid binding protein 4 (FABP4), Perilipin1, Adiponectin (AdipoQ), and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ), was enhanced in the degenerative cartilage of TMJ OA in UAC mice, accompanied by decreased expression of GDF11. After FFSS stimulation, there were fat droplets in the cytoplasm of cultured cells with increased expression of PPARγ, CEBPα, FABP4, Perilipin1, and AdipoQ and decreased expression of GDF11. Exogenous GDF11 inhibited increased lipid droplets and expression of AdipoQ, CEBPα, and FABP4 induced by FFSS stimulation. GDF11 did not affect the change in PPARγ expression under FFSS, but promoted its post-translational modification by small ubiquitin-related modifier (SUMOylation). Local injection of GDF11 alleviated TMJ OA-related cartilage degeneration and abnormal adipogenesis in UAC mice.
Conclusion: Abnormal adipogenesis of chondrocytes and decreased GDF11 expression were observed in degenerative cartilage of TMJ OA. GDF11 supplementation effectively inhibits the adipogenesis of chondrocytes and thus alleviates TMJ condylar cartilage degeneration. GDF11 may inhibit the abnormal adipogenesis of chondrocytes by affecting the SUMOylation of PPARγ. Cite this article: Bone Joint Res 2022;11(7):453-464.
Keywords: Cartilage degeneration; Chondrocyte; GDF11; Osteoarthritis; SUMOylation; Temporomandibular joint; adiponectin; cartilage tissue; chondrocytes; fatty acid binding protein; lipid; mesenchymal stem cells; rats; staining; temporomandibular joints.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Decreased expression of ATP-binding cassette protein G1 promotes abnormal adipogenesis of condylar chondrocytes in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis.J Oral Rehabil. 2024 May;51(5):805-816. doi: 10.1111/joor.13647. Epub 2023 Dec 26. J Oral Rehabil. 2024. PMID: 38146807
-
Chondrocyte-derived exosomes promote cartilage calcification in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2022 Feb 14;24(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s13075-022-02738-5. Arthritis Res Ther. 2022. PMID: 35164837 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of growth differentiation factor 11 on the steatosis of condylar chondrocytes in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritic mice.Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2022 Jan 25;40(1):14-21. doi: 10.7518/hxkq.2022.01.003. Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 38596988 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
-
Pathological mechanism of chondrocytes and the surrounding environment during osteoarthritis of temporomandibular joint.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Jun;25(11):4902-4911. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16514. Epub 2021 May 5. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 33949768 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Initiation and progression of dental-stimulated temporomandibular joints osteoarthritis.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2021 May;29(5):633-642. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2020.12.016. Epub 2021 Jan 8. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2021. PMID: 33422706 Review.
Cited by
-
Unbiased comparison and modularization identify time-related transcriptomic reprogramming in exercised rat cartilage: Integrated data mining and experimental validation.Front Physiol. 2022 Sep 15;13:974266. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.974266. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36187764 Free PMC article.
-
The mitochondrial E3 ligase MAPL SUMOylates Drp1 to facilitate mitochondrial fission in intervertebral disc degeneration.Bone Res. 2025 Aug 12;13(1):72. doi: 10.1038/s41413-025-00449-6. Bone Res. 2025. PMID: 40796734 Free PMC article.
-
Global Trends and Future Research Directions for Temporomandibular Disorders and Stem Cells.J Funct Biomater. 2023 Feb 13;14(2):103. doi: 10.3390/jfb14020103. J Funct Biomater. 2023. PMID: 36826902 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Critical signaling molecules in the temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis under different magnitudes of mechanical stimulation.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jul 11;15:1419494. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1419494. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39055494 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long-term hypoxic atmosphere enhances the stemness, immunoregulatory functions, and therapeutic application of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells.Bone Joint Res. 2024 Dec 12;13(12):764-778. doi: 10.1302/2046-3758.1312.BJR-2024-0136.R2. Bone Joint Res. 2024. PMID: 39662502 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

