When function is biological: Discerning how silver nanoparticle structure dictates antimicrobial activity
- PMID: 35789852
- PMCID: PMC9249613
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.104475
When function is biological: Discerning how silver nanoparticle structure dictates antimicrobial activity
Abstract
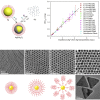
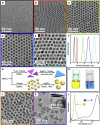
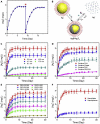
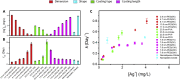
Silver nanomaterials have potent antibacterial properties that are the foundation for their wide commercial use as well as for concerns about their unintended environmental impact. The nanoparticles themselves are relatively biologically inert but they can undergo oxidative dissolution yielding toxic silver ions. A quantitative relationship between silver material structure and dissolution, and thus antimicrobial activity, has yet to be established. Here, this dissolution process and associated biological activity is characterized using uniform nanoparticles with variable dimension, shape, and surface chemistry. From this, a phenomenological model emerges that quantitatively relates material structure to both silver dissolution and microbial toxicity. Shape has the most profound influence on antibacterial activity, and surprisingly, surface coatings the least. These results illustrate how material structure may be optimized for antimicrobial properties and suggest strategies for minimizing silver nanoparticle effects on microbes.
Keywords: Microbiology; Nanomaterials; Nanoparticles; Nanotoxicology.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Antibacterial Activity of Silver Nanoparticles: Structural Effects.Adv Healthc Mater. 2018 Jul;7(13):e1701503. doi: 10.1002/adhm.201701503. Epub 2018 May 29. Adv Healthc Mater. 2018. PMID: 29808627 Review.
-
Mechanisms of Silver Nanoparticle Release, Transformation and Toxicity: A Critical Review of Current Knowledge and Recommendations for Future Studies and Applications.Materials (Basel). 2013 Jun 5;6(6):2295-2350. doi: 10.3390/ma6062295. Materials (Basel). 2013. PMID: 28809275 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A comparative study of silver nanoparticle dissolution under physiological conditions.Nanoscale Adv. 2020 Oct 20;2(12):5760-5768. doi: 10.1039/d0na00733a. eCollection 2020 Dec 15. Nanoscale Adv. 2020. PMID: 36133890 Free PMC article.
-
The dissolution and biological effects of silver nanoparticles in biological media.J Mater Chem B. 2014 Mar 28;2(12):1634-1643. doi: 10.1039/c3tb21569e. Epub 2014 Feb 13. J Mater Chem B. 2014. PMID: 32261391
-
Cytotoxicity induced by engineered silver nanocrystallites is dependent on surface coatings and cell types.Langmuir. 2012 Feb 7;28(5):2727-35. doi: 10.1021/la2042058. Epub 2012 Jan 23. Langmuir. 2012. PMID: 22216981
Cited by
-
Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Azadirachta indica and Syzygium aromaticum Extract and Its Antibacterial Action Against Enterococcus faecalis: An In Vitro Study.Cureus. 2024 Jul 21;16(7):e65044. doi: 10.7759/cureus.65044. eCollection 2024 Jul. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39165463 Free PMC article.
-
Mitigation of SARS-CoV-2 by Using Transition Metal Nanozeolites and Quaternary Ammonium Compounds as Antiviral Agents in Suspensions and Soft Fabric Materials.Int J Nanomedicine. 2023 May 3;18:2307-2324. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S396669. eCollection 2023. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023. PMID: 37163142 Free PMC article.
-
Silver Nanocube Epitaxy via Nanogap-Induced Electrostatics.Small Methods. 2025 Apr;9(4):e2401304. doi: 10.1002/smtd.202401304. Epub 2025 Feb 25. Small Methods. 2025. PMID: 39995345 Free PMC article.
-
Does Nanosilver Exposure Modulate Steroid Metabolism in the Testes?-A Possible Role of Redox Balance Disruption.Biomedicines. 2023 Dec 28;12(1):73. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12010073. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 38255180 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro Influence of ZnO, CrZnO, RuZnO, and BaZnO Nanomaterials on Bacterial Growth.Molecules. 2022 Nov 28;27(23):8309. doi: 10.3390/molecules27238309. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36500402 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbasi E., Milani M., Fekri Aval S., Kouhi M., Akbarzadeh A., Tayefi Nasrabadi H., Nikasa P., Joo S.W., Hanifehpour Y., Nejati-Koshki K., Samiei M. Silver nanoparticles: synthesis methods, bio-applications and properties. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2016;42:173–180. doi: 10.3109/1040841x.2014.912200. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Albalghiti E., Stabryla L.M., Gilbertson L.M., Zimmerman J.B. Towards resolution of antibacterial mechanisms in metal and metal oxide nanomaterials: a meta-analysis of the influence of study design on mechanistic conclusions. Environmental Science-Nano. 2021;8:37–66. doi: 10.1039/d0en00949k. - DOI
-
- Axson J.L., Stark D.I., Bondy A.L., Capracotta S.S., Maynard A.D., Philbert M.A., Bergin I.L., Ault A.P. Rapid kinetics of size and pH-dependent dissolution and aggregation of silver nanoparticles in simulated gastric fluid. J. Phys. Chem. C. 2015;119:20632–20641. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b03634. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

