IL-17 and IL-17-producing cells in protection versus pathology
- PMID: 35790881
- PMCID: PMC9255545
- DOI: 10.1038/s41577-022-00746-9
IL-17 and IL-17-producing cells in protection versus pathology
Abstract
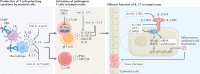
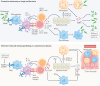
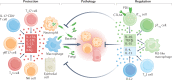
IL-17 cytokine family members have diverse biological functions, promoting protective immunity against many pathogens but also driving inflammatory pathology during infection and autoimmunity. IL-17A and IL-17F are produced by CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, γδ T cells, and various innate immune cell populations in response to IL-1β and IL-23, and they mediate protective immunity against fungi and bacteria by promoting neutrophil recruitment, antimicrobial peptide production and enhanced barrier function. IL-17-driven inflammation is normally controlled by regulatory T cells and the anti-inflammatory cytokines IL-10, TGFβ and IL-35. However, if dysregulated, IL-17 responses can promote immunopathology in the context of infection or autoimmunity. Moreover, IL-17 has been implicated in the pathogenesis of many other disorders with an inflammatory basis, including cardiovascular and neurological diseases. Consequently, the IL-17 pathway is now a key drug target in many autoimmune and chronic inflammatory disorders; therapeutic monoclonal antibodies targeting IL-17A, both IL-17A and IL-17F, the IL-17 receptor, or IL-23 are highly effective in some of these diseases. However, new approaches are needed to specifically regulate IL-17-mediated immunopathology in chronic inflammation and autoimmunity without compromising protective immunity to infection.
© 2022. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
K.H.G.M. is a co-founder and shareholder in a Biotech start-up company involved in the development of anti-inflammatory therapeutics.
Figures
References
-
- Rouvier E, Luciani MF, Mattéi MG, Denizot F, Golstein P. CTLA-8, cloned from an activated T cell, bearing AU-rich messenger RNA instability sequences, and homologous to a herpesvirus saimiri gene. J. Immunol. 1993;150:5445–5456. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

