Minos: variant adjudication and joint genotyping of cohorts of bacterial genomes
- PMID: 35791022
- PMCID: PMC9254434
- DOI: 10.1186/s13059-022-02714-x
Minos: variant adjudication and joint genotyping of cohorts of bacterial genomes
Abstract
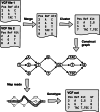
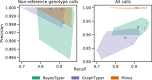
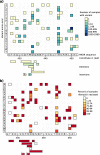
There are many short-read variant-calling tools, with different strengths and weaknesses. We present a tool, Minos, which combines outputs from arbitrary variant callers, increasing recall without loss of precision. We benchmark on 62 samples from three bacterial species and an outbreak of 385 Mycobacterium tuberculosis samples. Minos also enables joint genotyping; we demonstrate on a large (N=13k) M. tuberculosis cohort, building a map of non-synonymous SNPs and indels in a region where all such variants are assumed to cause rifampicin resistance. We quantify the correlation with phenotypic resistance and then replicate in a second cohort (N=10k).
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
E.R. is employed by the UK Health Security Agency and holds an honorary contract with Imperial College London. I.F.L. is Director of the Scottish Mycobacteria Reference Laboratory. S.N. receives funding from German Center for Infection Research, Excellenz Cluster Precision Medicine in Chronic Inflammation, Leibniz Science Campus Evolutionary Medicine of the LUNG (EvoLUNG)tion EXC 2167. P.S. is a consultant at Genoscreen. T.R. is funded by NIH and DoD and receives salary support from the non-profit organization FIND. T.R. is a co-founder, board member and shareholder of Verus Diagnostics Inc, a company that was founded with the intent of developing diagnostic assays. Verus Diagnostics was not involved in any way with data collection, analysis, or publication of the results. T.R. has not received any financial support from Verus Diagnostics. UCSD Conflict of Interest office has reviewed and approved T.R.’s role in Verus Diagnostics Inc. T.R. is a co-inventor of a provisional patent for a TB diagnostic assay (provisional patent #: 63/048.989). T.R. is a co-inventor on a patent associated with the processing of TB sequencing data (European Patent Application No. 14840432.0 & USSN 14/912,918). T.R. has agreed to “donate all present and future interest in and rights to royalties from this patent” to UCSD to ensure that he does not receive any financial benefits from this patent. S.S. is working and holding ESOPs at HaystackAnalytics Pvt. Ltd. (Product: Using whole genome sequencing for drug susceptibility testing for Mycobacterium tuberculosis). G.F.G. is listed as an inventor on patent applications for RBD-dimer-based CoV vaccines. The patents for RBD-dimers as protein subunit vaccines for SARS-CoV-2 have been licensed to Anhui Zhifei Longcom Biopharmaceutical Co. Ltd, China.
Figures
References
-
- Harris SR, Feil EJ, Holden MTG, Quail MA, Nickerson EK, Chantratita N, Gardete S, Tavares A, Day N, Lindsay JA, Edgeworth JD, de Lencastre H, Parkhill J, Peacock SJ, Bentley SD. Evolution of MRSA during hospital transmission and intercontinental spread. Science. 2010;327(5964):469–74. doi: 10.1126/science.1182395. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Holt KE, Wertheim H, Zadoks RN, Baker S, Whitehouse CA, Dance D, Jenney A, Connor TR, Hsu LY, Severin J, Brisse S, Cao H, Wilksch J, Gorrie C, Schultz MB, Edwards DJ, Nguyen KV, Nguyen TV, Dao TT, Mensink M, Minh VL, Nhu NTK, Schultsz C, Kuntaman K, Newton PN, Moore CE, Strugnell RA, Thomson NR. Genomic analysis of diversity, population structure, virulence, and antimicrobial resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae, an urgent threat to public health. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2015;112(27):3574–81. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1501049112. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Poplin R, Ruano-Rubio V, DePristo MA, Fennell TJ, Carneiro MO, Van der Auwera GA, Kling DE, Gauthier LD, Levy-Moonshine A, Roazen D, Shakir K, Thibault J, Chandran S, Whelan C, Lek M, Gabriel S, Daly MJ, Neale B, MacArthur DG, Banks E. Scaling accurate genetic variant discovery to tens of thousands of samples. bioRxiv. 2017. 10.1101/201178.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

