Changing global epidemiology of liver cancer from 2010 to 2019: NASH is the fastest growing cause of liver cancer
- PMID: 35793659
- PMCID: PMC9762323
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2022.05.003
Changing global epidemiology of liver cancer from 2010 to 2019: NASH is the fastest growing cause of liver cancer
Abstract
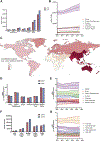
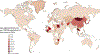
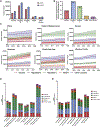
Liver cancer epidemiology is changing due to increasing alcohol consumption, rising prevalence of obesity, and advances in hepatitis B virus (HBV) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) treatment. However, the impact of these changes on global liver cancer burden remains unclear. We estimated global and regional temporal trends in the burden of liver cancer and the contributions of various liver disease etiologies using the methodology framework of the Global Burden of Disease study. Between 2010 and 2019, there was a 25% increase in liver cancer deaths. Age-standardized death rates (ASDRs) increased only in the Americas and remained stable or fell in all other regions. Between 2010 and 2019, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and alcohol had the fastest growing ASDRs, while HCV and HBV declined. Urgent measures are required at a global level to tackle underlying metabolic risk factors and slow the growing burden of NASH-associated liver cancer, especially in the Americas.
Keywords: alcohol; epidemiology; etiology; hepatitis B; hepatitis C; hepatocellular carcinoma; hepatoma; liver cancer; nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests R.L. serves as a consultant to Aardvark Therapeutics, Altimmune, Anylam/Regeneron, Amgen, Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myer Squibb, CohBar, Eli Lilly, Galmed, Gilead, Glympse Bio, Hightide, Inipharma, Intercept, Inventiva, Ionis, Janssen Inc., Madrigal, Metacrine, Inc., NGM Biopharmaceuticals, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Merck, Pfizer, Sagimet, Theratechnologies, 89 Bio, Terns Pharmaceuticals, and Viking Therapeutics and is cofounder of LipoNexus Inc. D.Q.H. has served as an advisory board member for Eisai. A.G.S. has served as a consultant or on advisory boards for Genentech, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Eisai, Exelixis, Wako Diagnostics, Exact Sciences, Roche, Glycotest, and GRAIL.
Figures
References
-
- Asrani SK, Devarbhavi H, Eaton J, and Kamath PS (2019). Burden of liver diseases in the world. J. Hepatol. 70, 151–171. - PubMed
-
- Dang H, Yeo YH, Yasuda S, Huang CF, Iio E, Landis C, Jun DW, Enomoto M, Ogawa E, Tsai PC, et al. (2020). Cure with interferon-free direct-acting antiviral is associated with increased survival in patients with hepatitis C virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma from both east and west. Hepatology 71, 1910–1922. - PubMed
-
- Desai N, Rich NE, Jain MK, Blackwell JM, Murphy CC, Perryman P, McBryde J, Quirk L, Clark C, Villarreal D, et al. (2021). Randomized clinical trial of inreach with or without mailed outreach to promote hepatitis C screening in a difficult-to-reach patient population. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 116, 976–983. - PubMed
-
- Dyson J, Jaques B, Chattopadyhay D, Lochan R, Graham J, Das D, Aslam T, Patanwala I, Gaggar S, Cole M, et al. (2014). Hepatocellular cancer: the impact of obesity, type 2 diabetes and a multidisciplinary team. J. Hepatol. 60, 110–117. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U01 DK130190/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA194307/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001442/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P42 ES010337/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK120515/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AA029019/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MD012565/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061734/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL147835/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK121378/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK106419/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA215520/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA230694/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK056338/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK124318/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

