SEMA4D/PlexinB1 promotes AML progression via activation of PI3K/Akt signaling
- PMID: 35794581
- PMCID: PMC9258142
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-022-03500-w
SEMA4D/PlexinB1 promotes AML progression via activation of PI3K/Akt signaling
Abstract
Background: Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is the most common type of acute leukemia in adults. SEMA4D is a 150 kDa transmembrane protein that belongs to the IV class of the subfamily of semaphorin family. Previous studies have reported that SEMA4D is a multifunctional target in many solid tumors, involving multiple physiological systems, and there are emerging therapies to target these pathways. The role of SEMA4D in AML has not yet been explored.
Methods: The SEMA4D expression prolile, clinical data and potential prognostic analysis were acquired via the cBioPortal and GEPIA databases. SEMA4D expression was measured using real-time quantitative PCR and western blot. Cell counting kit-8 (CCK8) and flow cytometry were used to evaluate the malignant biological characteristics.
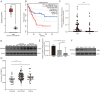
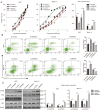
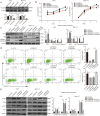
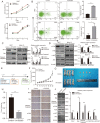
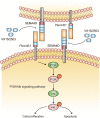
Results: We observed that SEMA4D was increased in AML patients and correlated with risk stratification and prognosis. Moreover, SEMA4D promotes the proliferation and inhibits apoptosis of AML cells by binding to its receptor, PlexinB1, and reduces the sensitivity of AML cells to daunorubicin. In addition, SEMA4D/PlexinB1 promotes the proliferation and survival of AML cells by activating the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. VX15/2503, an anti-SEMA4D antibody, can inhibit the proliferation of AML cells in xenograft mouse models, thereby inhibiting the development of AML.
Conclusion: SEMA4D will serve as a unique predictive biomarker and a possible therapeutic target in AML.
Keywords: Acute myeloid leukemia; PI3K/Akt; PlexinB1; Prognostic; SEMA4D.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

