Total hip arthroplasty after rotational acetabular osteotomy for developmental dysplasia of the hip: a retrospective observational study
- PMID: 35794611
- PMCID: PMC9258082
- DOI: 10.1186/s12891-022-05597-y
Total hip arthroplasty after rotational acetabular osteotomy for developmental dysplasia of the hip: a retrospective observational study
Abstract
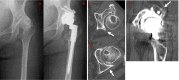
Background: Total hip arthroplasty after osteotomy is more technically challenging than primary total hip arthroplasty, especially concerning cup placement. This is attributed to bone morphological abnormalities caused by acetabular bone loss and osteophyte formation. This study aimed to investigate the clinical and radiological outcomes of total hip arthroplasty after rotational acetabular osteotomy compared with those of primary total hip arthroplasty, focusing mainly on acetabular deformity and cup position.
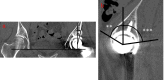
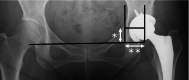
Methods: The study included 22 hips that had undergone rotational acetabular osteotomy and 22 hips in an age- and sex-matched control group of patients who underwent total hip arthroplasties between 2005 and 2020. We analyzed cup abduction and anteversion; lateral, anterior, and posterior cup center-edge angle; hip joint center position; femoral anteversion angle; and presence of acetabular defect using postoperative radiography and computed tomography. Operative results and clinical evaluations were also analyzed.
Results: The clinical evaluation showed that the postoperative flexion range of motion was lower in total hip arthroplasty after rotational acetabular osteotomy than in primary total hip arthroplasty, although no significant difference was noted in the postoperative total Japanese Orthopedic Association hip score. The operative time was significantly longer in the rotational acetabular osteotomy group than in the control group, but there was no significant difference in blood loss. The lateral cup center-edge angle was significantly higher and the posterior cup center-edge angle was significantly lower in the total hip arthroplasty after rotational acetabular osteotomy, suggesting a posterior bone defect existed in the acetabulum. In total hip arthroplasty after rotational acetabular osteotomy, the hip joint center was located significantly superior and lateral to the primary total hip arthroplasty.
Conclusions: In total hip arthroplasty after rotational acetabular osteotomy, the cup tended to be placed in the superior and lateral positions, where there was more bone volume. The deformity of the acetabulum and the high hip center should be considered for treatment success because they may cause cup instability, limited range of motion, and impingement.
Keywords: Bone defect; Developmental dysplasia; Hip center; Rotational acetabular osteotomy; Total hip arthroplasty.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rotational Acetabular Osteotomy for Pre- and Early Osteoarthritis Secondary to Dysplasia Provides Durable Results at 20 Years.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016 Oct;474(10):2145-53. doi: 10.1007/s11999-016-4854-8. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016. PMID: 27121873 Free PMC article.
-
Does Cup Position at the High Hip Center or Anatomic Hip Center in THA for Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip Result in Better Harris Hip Scores and Revision Incidence? A Systematic Review.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2021 May 1;479(5):1119-1130. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000001618. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2021. PMID: 33539054 Free PMC article.
-
The Safe Zone Range for Cup Anteversion Is Narrower Than for Inclination in THA.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2018 Feb;476(2):325-335. doi: 10.1007/s11999.0000000000000051. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2018. PMID: 29529664 Free PMC article.
-
Hip Morphology in Periacetabular Osteotomy (PAO) Patients Treated for Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip (DDH) as Infants Compared With Those Without Infant Treatment.J Pediatr Orthop. 2022 Jul 1;42(6):e565-e569. doi: 10.1097/BPO.0000000000002137. Epub 2022 Mar 10. J Pediatr Orthop. 2022. PMID: 35667051
-
Periacetabular osteotomy in the treatment of severe acetabular dysplasia. Surgical technique.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006 Mar;88 Suppl 1 Pt 1:65-83. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.E.00887. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006. PMID: 16510801 Review.
Cited by
-
Accelerometer-based portable navigation system shows no superior accuracy over pelvic alignment guide for acetabular cup placement in total hip arthroplasty in lateral decubitus position.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2024 Nov;144(11):4849-4856. doi: 10.1007/s00402-024-05571-4. Epub 2024 Sep 30. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2024. PMID: 39347968
References
-
- Yasunaga Y, Ochi M, Terayama H, Tanaka R, Yamasaki T, Ishii Y. Rotational acetabular osteotomy for advanced osteoarthritis secondary to dysplasia of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88:1915–1919. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

