Integrated bioinformatics analysis of validated and circulating miRNAs in ovarian cancer
- PMID: 35794700
- PMCID: PMC9299562
- DOI: 10.5808/gi.21067
Integrated bioinformatics analysis of validated and circulating miRNAs in ovarian cancer
Abstract
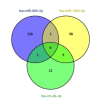
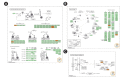
Recent studies have focused on the early detection of ovarian cancer (OC) using tumor materials by liquid biopsy. The mechanisms of microRNAs (miRNAs) to impact OC and signaling pathways are still unknown. This study aims to reliably perform functional analysis of previously validated circulating miRNAs' target genes by using pathfindR. Also, overall survival and pathological stage analyses were evaluated with miRNAs' target genes which are common in the The Cancer Genome Atlas and GTEx datasets. Our previous studies have validated three downregulated miRNAs (hsa-miR-885-5p, hsa-miR-1909-5p, and hsalet7d-3p) having a diagnostic value in OC patients' sera, with high-throughput techniques. The predicted target genes of these miRNAs were retrieved from the miRDB database (v6.0). Active-subnetwork-oriented Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment analysis was conducted by pathfindR using the target genes. Enrichment of KEGG pathways assessed by the analysis of pathfindR indicated that 24 pathways were related to the target genes. Ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis, spliceosome and Notch signaling pathway were the top three pathways with the lowest p-values (p < 0.001). Ninety-three common genes were found to be differentially expressed (p < 0.05) in the datasets. No significant genes were found to be significant in the analysis of overall survival analyses, but 24 genes were found to be significant with pathological stages analysis (p < 0.05). The findings of our study provide in-silico evidence that validated circulating miRNAs' target genes and enriched pathways are related to OC and have potential roles in theranostics applications. Further experimental investigations are required to validate our results which will ultimately provide a new perspective for translational applications in OC management.
Keywords: KEGG pathway; integrative analysis; microRNAs; ovarian cancer; pathfindR.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures


References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
