Basal and Stress-Induced Network Activity in the Adrenal Medulla In Vivo
- PMID: 35795145
- PMCID: PMC9250985
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.875865
Basal and Stress-Induced Network Activity in the Adrenal Medulla In Vivo
Abstract
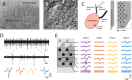
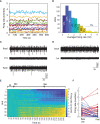
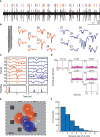
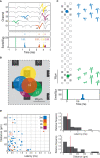
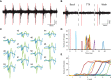
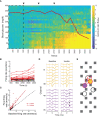
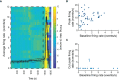
The adrenal medulla plays a critical role in mammalian homeostasis and the stress response. It is populated by clustered chromaffin cells that secrete epinephrine or norepinephrine along with peptides into the bloodstream affecting distant target organs. Despite been heavily studied, the central control of adrenal medulla and in-situ spatiotemporal responsiveness remains poorly understood. For this work, we continuously monitored the electrical activity of individual adrenomedullary chromaffin cells in the living anesthetized rat using multielectrode arrays. We measured the chromaffin cell activity under basal and physiological stress conditions and characterized the functional micro-architecture of the adrenal medulla. Under basal conditions, chromaffin cells fired action potentials with frequencies between ~0.2 and 4 Hz. Activity was almost completely driven by sympathetic inputs coming through the splanchnic nerve. Chromaffin cells were organized into independent local networks in which cells fired in a specific order, with latencies from hundreds of microseconds to a few milliseconds. Electrical stimulation of the splanchnic nerve evoked almost exactly the same spatiotemporal firing patterns that occurred spontaneously. Hypoglycemic stress, induced by insulin administration resulted in increased activity of a subset of the chromaffin cells. In contrast, respiratory arrest induced by lethal anesthesia resulted in an increase in the activity of virtually all chromaffin cells before cessation of all activity. These results suggest a stressor-specific activation of adrenomedullary chromaffin cell networks and revealed a surprisingly complex electrical organization that likely reflects the dynamic nature of the adrenal medulla's neuroendocrine output during basal conditions and during different types of physiological stress.
Keywords: adrenal medulla; chromaffin cell; electrophysiology; in-vivo; stress response.
Copyright © 2022 Lopez Ruiz, Ernst, Holz and Stuenkel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Spatial and activity-dependent catecholamine release in rat adrenal medulla under native neuronal stimulation.Physiol Rep. 2016 Sep;4(17):e12898. doi: 10.14814/phy2.12898. Physiol Rep. 2016. PMID: 27597763 Free PMC article.
-
PACAP regulates immediate catecholamine release from adrenal chromaffin cells in an activity-dependent manner through a protein kinase C-dependent pathway.J Neurochem. 2009 Aug;110(4):1214-25. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.06206.x. Epub 2009 Jun 5. J Neurochem. 2009. PMID: 19508428 Free PMC article.
-
Electrophysiological and morphological features underlying neurotransmission efficacy at the splanchnic nerve-chromaffin cell synapse of bovine adrenal medulla.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2010 Feb;298(2):C397-405. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00440.2009. Epub 2009 Nov 25. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2010. PMID: 19940070
-
Cholinergic and peptidergic neurotransmission in the adrenal medulla: A dynamic control of stimulus-secretion coupling.IUBMB Life. 2020 Apr;72(4):553-567. doi: 10.1002/iub.2117. Epub 2019 Jul 13. IUBMB Life. 2020. PMID: 31301221 Review.
-
Ontogeny of O2 and CO2//H+ chemosensitivity in adrenal chromaffin cells: role of innervation.J Exp Biol. 2014 Mar 1;217(Pt 5):673-81. doi: 10.1242/jeb.086165. J Exp Biol. 2014. PMID: 24574383 Review.
Cited by
-
New insights about non-neurogenic excitability revealed by MEA recordings from rat adrenal chromaffin cells.Pflugers Arch. 2023 Feb;475(2):151-152. doi: 10.1007/s00424-022-02783-8. Epub 2022 Dec 22. Pflugers Arch. 2023. PMID: 36547699 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Catecholamine concentration as a predictor of mortality in emergency surgical patients.Int J Emerg Med. 2024 Jul 18;17(1):95. doi: 10.1186/s12245-024-00676-4. Int J Emerg Med. 2024. PMID: 39026158 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular mechanisms underlying pituitary adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide-stimulated secretion in the adrenal medulla.Biochem Soc Trans. 2024 Dec 19;52(6):2373-2383. doi: 10.1042/BST20231326. Biochem Soc Trans. 2024. PMID: 39656194 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Developmental Changes in Gap Junction Expression in Rat Adrenal Medullary Chromaffin Cells.Acta Histochem Cytochem. 2024 Dec 20;57(6):189-197. doi: 10.1267/ahc.24-00033. Epub 2024 Dec 11. Acta Histochem Cytochem. 2024. PMID: 39776934 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

