Clinical Characteristics of Patients With HNF1-alpha MODY: A Literature Review and Retrospective Chart Review
- PMID: 35795147
- PMCID: PMC9252268
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.900489
Clinical Characteristics of Patients With HNF1-alpha MODY: A Literature Review and Retrospective Chart Review
Abstract
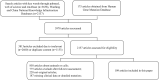
The clinical manifestation of hepatocyte nuclear factor-1-alpha (HNF1-alpha) maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY) is highly variable. This study aims to investigate the clinical characteristics of patients with HNF1-alpha MODY in general, by geographical regions (Asian or non-Asian), HNF1-alpha mutations, and islet autoantibody status. A literature review and a chart review of patients with HNF1-alpha MODY were performed. The means and proportions from studies were pooled using the inverse variance method for pooling, and subgroup analyses were performed. A total of 109 studies involving 1,325 patients [41.5%, 95% confidence interval (CI): 35.2, 48.1; male] were identified. The mean age of diagnosis was 20.3 years (95% CI: 18.3-22.2), and the mean glycated hemoglobin was 7.3% (95% CI: 7.2-7.5). In comparison, Asian patients exhibited significantly higher HbA1c (p = 0.007) and 2-h post-load C-peptide (p = 0.012) levels and lower levels of triglyceride (TG) (p < 0.001), total cholesterol (TC) (p < 0.001), and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-c) (p < 0.001) and less often had macrovascular complications (p = 0.014). The age of diagnosis was oldest in patients with mutations in the transactivation domain (p < 0.001). The levels of 2-h post-load C-peptide (p < 0.001), TG (p = 0.007), TC (p = 0.017), and HDL-c (p = 0.001) were highest and the prevalence of diabetic neuropathy was lowest (p = 0.024) in patients with DNA-binding domain mutations. The fasting (p = 0.004) and 2-h post-load glucose (p = 0.003) levels and the prevalence of diabetic neuropathy (p = 0.010) were higher among patients with positive islet autoantibodies. The study demonstrated that the clinical manifestations of HNF1-alpha MODY differed by geographical regions, HNF1-alpha mutations, and islet autoantibody status.
Keywords: HNF1-alpha MODY; HNF1-alpha mutations; diabetes; diabetic complication; pancreatic islet autoantibody.
Copyright © 2022 Zhao, Ding, Yang, Sun, Wang, Li and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Losekoot M, Broekman A, Breuning M, De Koning E, Romijn J, Maassen J. Molecular Diagnosis on Indication of Maturity Onset Diabetes of the Young; Results From 184 Patients. Nederlands Tijdschrift Voor Geneeskunde. (2005) 149(3):139–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous