Analysis of Medication Rule of Primary Epilepsy Based on Xiaocheng Yan's Clinical Experience Collection of Epilepsy
- PMID: 35795265
- PMCID: PMC9252657
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/9539944
Analysis of Medication Rule of Primary Epilepsy Based on Xiaocheng Yan's Clinical Experience Collection of Epilepsy
Abstract
Objective: To explore and analyze the medication rule of Professor Xiaocheng Yan in the treatment of primary epilepsy, hoping to provide reference for the clinical treatment of primary epilepsy.
Methods: Mining and analysis of Professor Xiaocheng Yan sorted out the medical cases of primary epilepsy in Xiaocheng Yan's clinical experience collection of epilepsy, extracted the traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) prescription data in the medical cases, standardized the obtained TCM prescription data, and used the data mining function integrated by the ancient and modern medical case cloud platform V2.3.5 to carry out frequency statistics, cluster analysis, association analysis, and complex network analysis on the TCM data, and the common herbs used by Professor Xiaocheng Yan in the treatment of primary epilepsy, properties and classifications of commonly used herbs, pairs of commonly used herbs, and core prescriptions were obtained.
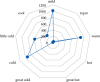
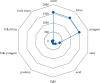
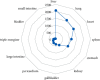
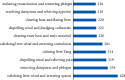
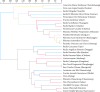
Results: A total of 39 cases, 228 medical records, and 230 prescriptions data of TCM were included. A total of 96 Chinese medicinal herbs were involved, and the total frequency of medication was 3,828. High-frequency herbs include Rhizoma Gastrodiae (Tianma) (222 times), Ramulus Uncariae cum Uncis (Gouteng) (220 times), Rhizoma Acori Tatarinowii (Shichangpu) (216 times), Rhizoma Pinelliae Praeparatum (Fabanxia) (207 times), Bombyx Batryticatus (Jiangcan) (206 times), and Periostracum Cicadae (Chantui) (181 times). The main properties and flavors of commonly used Chinese medicinal herbs were sweet, bitter, and pungent, which were mainly attributed to the four meridians of liver, lung, heart, and spleen. Commonly used couplet herbs were {Periostracum Cicadae (Chantui)} ≥ {Bombyx Batryticatus (Jiangcan)}, {Rhizoma Acori Tatarinowii (Shichangpu)} ≥{ Bombyx Batryticatus (Jiangcan)}, {Radix Bupleuri (Chaihu)} ≥ {Radix Scutellariae (Huangqin)}, {Rhizoma Gastrodiae (Tianma)} ≥ {Ramulus Uncariae cum Uncis (Gouteng)}, {Rhizoma Acori Tatarinowii (Shichangpu)} ≥ {Periostracum Cicadae (Chantui)}, {Ramulus Uncariae cum Uncis (Gouteng)} ≥ {Bombyx Batryticatus (Jiangcan)}, {Bombyx Batryticatus (Jiangcan)} ≥ {Rhizoma Gastrodiae (Tianma)}, {Rhizoma Acori Tatarinowii (Shichangpu)} ≥ {Ramulus Uncariae cum Uncis (Gouteng)}, etc. The core prescription composition was based on the addition and subtraction of Tianma Gouteng decoction and Erchen decoction. The main pharmacological mechanisms of core prescriptions are mainly reflected in antioxidation, enhancing GABA efficacy, and regulating NMDA channel and sodium channel, neuroprotection, and so on.
Conclusion: Professor Xiaocheng Yan's medication for the treatment of primary epilepsy was based on the principle of relieving wind and spasm, drying dampness and resolving phlegm, giving consideration to both Qi and blood, and harmonizing liver, lung, heart, and spleen.
Copyright © 2022 Yu Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Figures


References
-
- Chinese Medical Association. Clinical Guidelines For Diagnosis and Treatment of Epilepsy . Beijing, China: People’s Health Publishing House; 2018.
-
- Miao A. L., Wang X. S. Diagnosis and treatment of epilepsy. Journal of Clinical Medicine . 2013;13(12):797–799.
-
- Jia J. P., Chen S. D. Neurology . Beijing, China: People’s Health Publishing House; 2013.
-
- Yang Y. F., Xia L. B. Diagnosis and Treatment of Epilepsy . Taiyuan, China: Shanxi Science and Technology Press; 1997.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

