Predictive Value of Non-high-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol and Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio for Coronary Artery Vulnerable Plaques in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- PMID: 35795369
- PMCID: PMC9251121
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.927768
Predictive Value of Non-high-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol and Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio for Coronary Artery Vulnerable Plaques in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
Background: Patients with diabetes have an increased risk of developing vulnerable plaques (VPs), in which dyslipidemia and chronic inflammation play important roles. Non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (non-HDL-C) and neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) have emerged as potential markers of both coronary artery VPs and cardiovascular prognosis. This study aimed to investigate the predictive value of non-HDL-C and NLR for coronary artery VPs in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods: We retrospectively enrolled 204 patients with T2DM who underwent coronary computed tomography angiography between January 2018 and June 2020. Clinical data including age, sex, hypertension, smoking, total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, HDL-C, triglyceride, non-HDL-C, glycated hemoglobin, neutrophil count, lymphocyte count, NLR, and platelet count were analyzed. Multivariate logistic regression was used to estimate the association between non-HDL-C, NLR, and coronary artery VPs. Receiver operating curve analysis was performed to evaluate the value of non-HDL-C, NLR, and their combination in predicting coronary artery VPs.
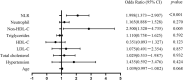
Results: In our study, 67 patients (32.84%) were diagnosed with VPs, 75 (36.77%) with non-VP, and 62 (30.39%) with no plaque. Non-HDL-C and NLR were independent risk factors for coronary artery VPs in patients with T2DM. The areas under the ROC curve of non-HDL-C, NLR, and their combination were 0.748 [95% confidence interval (CI): 0.676-0.818], 0.729 (95% CI: 0.650-0.800), and 0.825 (95% CI: 0.757-0.887), respectively.
Conclusion: Either non-HDL-C or NLR could be used as a predictor of coronary artery VPs in patients with T2DM, but the predictive efficiency and sensitivity of their combination would be better.
Keywords: coronary computed tomography angiography; coronary heart disease; neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio; non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; type 2 diabetes mellitus; vulnerable plaque.
Copyright © 2022 Huang, Yang, Zhao, Chen, Pan, Lai, Ouyang, Deng, Du, Li, Hu, Guo and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Correlation between neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio combined with low-density lipoprotein cholesterol/high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and severity of coronary artery disease in patients with acute coronary syndrome].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2022 Mar;34(3):274-279. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20211008-01441. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2022. PMID: 35574745 Chinese.
-
The relationship between NLR, LDL-C/HDL-C, NHR and coronary artery disease.PLoS One. 2024 Jul 10;19(7):e0290805. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0290805. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38985788 Free PMC article.
-
Novel nomogram for predicting coronary vulnerable plaque risk in patients with coronary artery disease.Biomark Med. 2022 Nov;16(16):1139-1149. doi: 10.2217/bmm-2022-0855. Epub 2023 Jan 10. Biomark Med. 2022. PMID: 36625283
-
Utility of neutrophil-to-high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol ratio in patients with coronary artery disease: a narrative review.J Int Med Res. 2023 Apr;51(4):3000605231166518. doi: 10.1177/03000605231166518. J Int Med Res. 2023. PMID: 37038922 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systemic Review to Explore the Effect of Dyslipidaemia and Metabolic Function in Coronary Heart Disease with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: In Tertiary Care Center.J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2025 May;17(Suppl 1):S127-S129. doi: 10.4103/jpbs.jpbs_1976_24. Epub 2025 Mar 6. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2025. PMID: 40511160 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Risk factors and the CCTA application in patients with vulnerable coronary plaque in type 2 diabetes: a retrospective study.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024 Feb 4;24(1):89. doi: 10.1186/s12872-024-03717-1. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024. PMID: 38311736 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional profiles associated with coronary artery disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Apr 19;15:1323168. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1323168. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38706700 Free PMC article.
-
The Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio Predicts Diabetic Retinopathy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2022 Nov 22;15:3617-3626. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S378284. eCollection 2022. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2022. PMID: 36444389 Free PMC article.
-
High neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio with type 2 diabetes mellitus predicts poor prognosis in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention: a large-scale cohort study.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2022 Aug 13;21(1):156. doi: 10.1186/s12933-022-01583-9. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2022. PMID: 35964050 Free PMC article.
-
Lymphocyte-to-high-density lipoprotein ratio and mortality in asthma patients: a novel immunoinflammatory biomarker with nonlinear association.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Jun 13;12:1553188. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1553188. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40584718 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Henning RJ. Type-2 diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular disease. Future Cardiol. (2018) 14:491–509. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

