Antibody and T-Cell Responses 6 Months After Coronavirus Disease 2019 Messenger RNA-1273 Vaccination in Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease, on Dialysis, or Living With a Kidney Transplant
- PMID: 35796536
- PMCID: PMC9278186
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/ciac557
Antibody and T-Cell Responses 6 Months After Coronavirus Disease 2019 Messenger RNA-1273 Vaccination in Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease, on Dialysis, or Living With a Kidney Transplant
Abstract
Background: The immune response to COVID-19 vaccination is inferior in kidney transplant recipients (KTRs) and to a lesser extent in patients on dialysis or with chronic kidney disease (CKD). We assessed the immune response 6 months after mRNA-1273 vaccination in kidney patients and compared this to controls.
Methods: A total of 152 participants with CKD stages G4/5 (eGFR <30 mL/min/1.73 m2), 145 participants on dialysis, 267 KTRs, and 181 controls were included. SARS-CoV-2 Spike S1 specific IgG antibodies were measured using fluorescent bead-based multiplex-immunoassay, neutralizing antibodies to ancestral, Delta, and Omicron (BA.1) variants by plaque reduction, and T-cell responses by interferon-γ release assay.
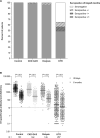
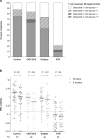
Results: At 6 months after vaccination, S1-specific antibodies were detected in 100% of controls, 98.7% of CKD G4/5 patients, 95.1% of dialysis patients, and 56.6% of KTRs. These figures were comparable to the response rates at 28 days, but antibody levels waned significantly. Neutralization of the ancestral and Delta variants was detected in most participants, whereas neutralization of Omicron was mostly absent. S-specific T-cell responses were detected at 6 months in 75.0% of controls, 69.4% of CKD G4/5 patients, 52.6% of dialysis patients, and 12.9% of KTRs. T-cell responses at 6 months were significantly lower than responses at 28 days.
Conclusions: Although seropositivity rates at 6 months were comparable to rates at 28 days after vaccination, significantly decreased antibody levels and T-cell responses were observed. The combination of low antibody levels, reduced T-cell responses, and absent neutralization of the newly emerging variants indicates the need for additional boosts or alternative vaccination strategies in KTRs.
Clinical trials registration: NCT04741386.
Keywords: COVID-19; chronic kidney disease; dialysis; kidney transplantation; mRNA-1273 vaccine.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflicts of interest. C. C. B. reports a Dutch Kidney Foundation grant and support from the Procare II study unrelated to this work and a role as Executive Editor/Social Media Editor for Transplantation Journal. M. M. L. K. reports participation on an advisory board on maribavir for Takeda. All other authors report no potential conflicts.All authors have submitted the ICMJE Form for Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest. Conflicts that the editors consider relevant to the content of the manuscript have been disclosed.
Figures



References
-
- Kho MML, Reinders MEJ, Baan CC, et al. . The RECOVAC IR study: the immune response and safety of the mRNA-1273 COVID-19 vaccine in patients with chronic kidney disease, on dialysis, or living with a kidney transplant—a prospective, controlled, multicenter observational cohort by the REnal patients COVID-19 VACcination (RECOVAC) consortium COVID-19 VACcination (RECOVAC) consortium. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2021; 36:1761–4. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

