Diabetic health literacy and associated factors among diabetes mellitus patients on follow up at public hospitals, Bale Zone, South East Ethiopia, 2021
- PMID: 35797276
- PMCID: PMC9262198
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0270161
Diabetic health literacy and associated factors among diabetes mellitus patients on follow up at public hospitals, Bale Zone, South East Ethiopia, 2021
Abstract
Objective: This study was aimed to assess diabetic health literacy and associated factors among adult diabetic patients in public hospitals, Bale Zone, Southeast Ethiopia.
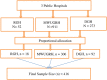
Methods: A hospital-based cross-sectional study was conducted among 402 diabetic patients in three public hospitals and the samples were selected using simple random sampling technique. The comprehensive functional, communicative, and critical health literacy questionnaire was used to measure diabetic health literacy. Descriptive statistics and Ordinary logistic regression analyses were conducted, and a P-value of < 0.05 was considered to declare a result as statistically significant.
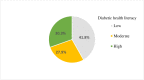
Result: A total of 402 diabetic patients were involved in the study. Of all respondents, 41.8%, 27.9%, and 30.3% had low, moderate, and high diabetic health literacy respectively. Educational status; can't read and write (AOR = 0.085;95% CI: 0.03,0.26), can read and write (AOR = 0.10; 95% CI: 0.04,0.30), primary school (AOR = 0.25; 95% CI: 0.09,0.67), secondary school (AOR = 0.37; 95% CI: 0.14,0.99), duration of onset ≤5 years (AOR = 2.05; 95% CI:1.09,4.19), being not member of DM association (AOR = 0.43; 95% CI: 0.26,0.73), having ≤ 3 diabetes mellitus information sources (AOR = 0.15; 95% CI: 0.03,0.77), social support; poor (AOR = 0.40;95% CI: 0.21,0.79), and moderate (AOR = 0.50; 95% CI: 0.28,0.92) were significantly associated with diabetic health literacy.
Conclusion: A substantial number of diabetic patients had low diabetic health literacy. Educational status, Sources of diabetic information, Member of DM association, and social support were significantly and positively associated with diabetic health literacy. But, duration of diabetes onset was negatively associated with diabetic health literacy of respondents. So, we recommend providing readable and picturized printed materials, and diabetic patient education to be considered.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- WHO, World Health Organization Global report on diabetes. World Health Organization 2016. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/204871.
-
- IDF, International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas, 9th edn. Brussels, Belgium:., 2019. https://www.diabetesatlas.org.
-
- Mukanoheli V., et al., Functional Health Literacy and Self-Care Behaviors Among Type 2 Diabetic Patients at a University Teaching Hospital in Kigali. Rwanda Journal of Medicine and Health Sciences, 2020. 3(1): p. 49–59.
-
- Kinfe G., et al., Diabetes in Ethiopia: A systematic review of prevalence, risk factors, complications, and cost. Obesity Medicine 2019. 15(100132).
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical