Mycobacteriophages: From Petri dish to patient
- PMID: 35797343
- PMCID: PMC9262239
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010602
Mycobacteriophages: From Petri dish to patient
Abstract
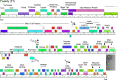
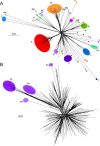
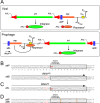
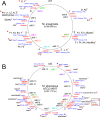
Mycobacteriophages-bacteriophages infecting Mycobacterium hosts-contribute substantially to our understanding of viral diversity and evolution, provide resources for advancing Mycobacterium genetics, are the basis of high-impact science education programs, and show considerable therapeutic potential. Over 10,000 individual mycobacteriophages have been isolated by high school and undergraduate students using the model organism Mycobacterium smegmatis mc2155 and 2,100 have been completely sequenced, giving a high-resolution view of the phages that infect a single common host strain. The phage genomes are revealed to be highly diverse and architecturally mosaic and are replete with genes of unknown function. Mycobacteriophages have provided many widely used tools for Mycobacterium genetics including integration-proficient vectors and recombineering systems, as well as systems for efficient delivery of reporter genes, transposons, and allelic exchange substrates. The genomic insights and engineering tools have facilitated exploration of phages for treatment of Mycobacterium infections, although their full therapeutic potential has yet to be realized.
Conflict of interest statement
I have read the journal’s policy and have the following conflicts: I receive research support from Janssen Pharmaceuticals, and am a consultant for Tessera Inc. and Janssen.
Figures
References
-
- Rohwer F, Youle M, Maughan H, Hisakawa N. Life in our phage world: A centenial field guide to the earth’s most diverse inhiabitants. San Diego, CA: Wholon; 2014.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

