Plasma proteomic analysis to identify potential biomarkers of histologic chorioamnionitis in women with preterm premature rupture of membranes
- PMID: 35797368
- PMCID: PMC9262229
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0270884
Plasma proteomic analysis to identify potential biomarkers of histologic chorioamnionitis in women with preterm premature rupture of membranes
Abstract
Introduction: To identify potential biomarkers in the plasma that could predict histologic chorioamnionitis (HCA) in women with preterm premature rupture of membranes (PPROM), using shotgun and targeted proteomic analyses.
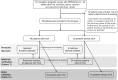
Methods: This retrospective cohort study included 78 singleton pregnant women with PPROM (24-34 gestational weeks) who delivered within 96 h of blood sampling. Maternal plasma samples were analyzed by label-free liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry for proteome profiling in a nested case-control study design (HCA cases vs. non-HCA controls [n = 9 each]). Differential expression of 12 candidate proteins was assessed by multiple reaction monitoring-mass spectrometry (MRM-MS) analysis in individual plasma samples from cases and controls matched by gestational age at sampling (n = 40, cohort 1). A validation study was further performed in an independent study group (n = 38, cohort 2) using ELISA and turbidimetric immunoassay for three differentially expressed proteins.
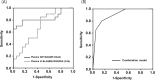
Results: Shotgun proteomics analyses yielded 18 proteins that were differentially expressed (P < 0.05) between HCA cases and non-HCA controls. MRM-MS analysis of 12 differentially expressed proteins further revealed that the CRP, C4A, and SAA4 levels were significantly increased in women with HCA. A multi-marker panel comprising plasma SAA4 and C4A showed enhanced potential for differentiating HCA from non-HCA women (area under the curve = 0.899). Additional validation of these findings by ELISA assays revealed that the CRP levels were significantly higher in women with HCA than in those without HCA, whereas the plasma levels of C4A and SAA4 did not significantly differ between the two groups.
Conclusions: Plasma C4A, SAA4, and CRP were identified as potential biomarkers for detecting HCA in women with PPROM, based on targeted and shotgun proteomic analyses, showing good accuracy when used as a combined dual-biomarker panel (C4A and SAA4). Nevertheless, ELISA validation of these proteins, except for CRP, may not yield clinically useful markers for predicting HCA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

