Therapeutic in vivo delivery of gene editing agents
- PMID: 35798006
- PMCID: PMC9454337
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2022.03.045
Therapeutic in vivo delivery of gene editing agents
Abstract
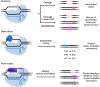
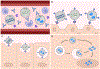
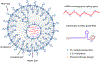
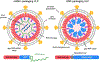
In vivo gene editing therapies offer the potential to treat the root causes of many genetic diseases. Realizing the promise of therapeutic in vivo gene editing requires the ability to safely and efficiently deliver gene editing agents to relevant organs and tissues in vivo. Here, we review current delivery technologies that have been used to enable therapeutic in vivo gene editing, including viral vectors, lipid nanoparticles, and virus-like particles. Since no single delivery modality is likely to be appropriate for every possible application, we compare the benefits and drawbacks of each method and highlight opportunities for future improvements.
Copyright © 2022. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors have filed patent applications on gene editing technologies and delivery technologies through the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard. S.B. is a scientific cofounder and an employee of Nvelop Therapeutics. D.R.L. is a consultant and cofounder of Beam Therapeutics, Prime Medicine, Pairwise Plants, Editas Medicine, Chroma Medicine, and Nvelop Therapeutics, companies that use and/or deliver genome editing or genome engineering agents.
Figures

References
-
- Adams D, Gonzalez-Duarte A, O'Riordan WD, Yang CC, Ueda M, Kristen AV, Tournev I, Schmidt HH, Coelho T, Berk JL, et al. (2018). Patisiran, an RNAi Therapeutic, for Hereditary Transthyretin Amyloidosis. N Engl J Med 379, 11–21. - PubMed
-
- Akinc A, Maier MA, Manoharan M, Fitzgerald K, Jayaraman M, Barros S, Ansell S, Du X, Hope MJ, Madden TD, et al. (2019). The Onpattro story and the clinical translation of nanomedicines containing nucleic acid-based drugs. Nat Nanotechnol 14, 1084–1087. - PubMed
-
- Anzalone AV, Koblan LW, and Liu DR (2020). Genome editing with CRISPR-Cas nucleases, base editors, transposases and prime editors. Nat Biotechnol 38, 824–844. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

