Data modelling recipes for SARS-CoV-2 wastewater-based epidemiology
- PMID: 35798267
- PMCID: PMC9252867
- DOI: 10.1016/j.envres.2022.113809
Data modelling recipes for SARS-CoV-2 wastewater-based epidemiology
Abstract
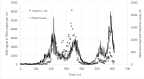
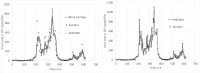
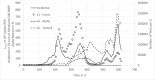
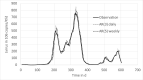
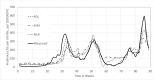
Wastewater based epidemiology is recognized as one of the monitoring pillars, providing essential information for pandemic management. Central in the methodology are data modelling concepts for both communicating the monitoring results but also for analysis of the signal. It is due to the fast development of the field that a range of modelling concepts are used but without a coherent framework. This paper provides for such a framework, focusing on robust and simple concepts readily applicable, rather than applying latest findings from e.g., machine learning. It is demonstrated that data preprocessing, most important normalization by means of biomarkers and equal temporal spacing of the scattered data, is crucial. In terms of the latter, downsampling to a weekly spaced series is sufficient. Also, data smoothing turned out to be essential, not only for communication of the signal dynamics but likewise for regressions, nowcasting and forecasting. Correlation of the signal with epidemic indicators requires multivariate regression as the signal alone cannot explain the dynamics but - for this case study - multiple linear regression proofed to be a suitable tool when the focus is on understanding and interpretation. It was also demonstrated that short term prediction (7 days) is accurate with simple models (exponential smoothing or autoregressive models) but forecast accuracy deteriorates fast for longer periods.
Keywords: Data modelling; Forecast; Regression; SARS-CoV-2; Smoothing; Wastewater-based epidemiology.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- Ahmed W., Angel N., Edson J., Bibby K., Bivins A., O'Brien J.W., Choi P.M., Kitajima M., Simpson S.L., Li J., Tscharke B. First confirmed detection of SARS-CoV-2 in untreated wastewater in Australia: a proof of concept for the wastewater surveillance of COVID-19 in the community. Sci. Total Environ. 2020;728 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Amman F., Markt R., Endler L., Agerer B., Schedl A., Richter L., Zechmeister M., Bicher M., Heiler G., Triska P., Thornton M., Penz Th, Senekowitsch M., Laine J., Keszei Z., Klimek P., Nägele F., Mayr M., Daleiden B., Steinlechner M., Niederstätter H., Heidinger P., Rauch W., Scheffknecht Ch, Vogl G., Weichlinger G., Wagner A., Slipko K., Masseron A., Radu E., Allerberger F., Popper N., Bock Ch, Schmid D., Oberacher H., Kreuzinger N., Insam H., Bergthaler A. Viral variant-resolved wastewater surveillance of SARS-CoV-2 at national scale. Nat. Biotechnol. 2022 doi: 10.1038/s41587-022-01387-y. In press. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Arabzadeh R., Gruenbacher D.M., Insam H., Kreuzinger N., Markt R., Rauch W. Data filtering methods for SARS-CoV-2 wastewater surveillance. Water Sci. Technol. 2021;84(6):1324–1339. (2021) - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

