Meta-analysis of COVID-19 prevalence during preoperative COVID-19 screening in asymptomatic patients
- PMID: 35798523
- PMCID: PMC9263349
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-058389
Meta-analysis of COVID-19 prevalence during preoperative COVID-19 screening in asymptomatic patients
Abstract
Objectives: Patients with COVID-19 may be asymptomatic and are able to transmit COVID-19 during a surgical procedure, resulting in increased pressure on healthcare and reduced control of COVID-19 spread. There remains uncertainty about the implementation of preoperative screening for COVID-19 in asymptomatic surgical patients. Therefore, this study aims to determine the prevalence of preoperative COVID-19, confirmed by reverse transcriptase PCR (RT-PCR), in asymptomatic patients.
Design: Systematic review and meta-analysis.
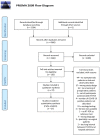
Data sources: Pubmed and Embase databases were searched through 20 February 2022.
Eligibility criteria: All COVID-19 articles including preoperative asymptomatic patients were included.
Data extraction and synthesis: Two independent reviewers extracted data and assessed risk of bias. Meta-analysis was performed to determine the prevalence of COVID-19 with 95% CI. Moreover, estimated positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value, false-positives (FP) and false-negatives were calculated for preoperative asymptomatic patients.
Results: Twenty-seven studies containing 27 256 asymptomatic preoperative screened patients were included, of which 431 were positive for COVID-19 by RT-PCR test. In addition, the meta-analysis revealed a pooled COVID-19 prevalence of 0.76% (95% CI 0.36% to 1.59%). The calculated PPV for this prevalence is 40.8%.
Conclusions: The pooled COVID-19 prevalence in asymptomatic patients tested preoperatively was 0.76%, with low corresponding PPV. Consequently, nearly three-quarters of postponed surgical procedures in asymptomatic preoperative patients may be FP. In the event of similar pandemics, modification of preoperative mandatory RT-PCR COVID-19 testing in asymptomatic patients may be considered.
Keywords: COVID-19; infection control; surgery.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2022. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization . WHO coronavirus (COVID-19) dashboard [online]. Available: https://covid19.who.int [Accessed 12 Apr 2021].
-
- NVVH . Handle for surgical procedures during corona crisis [online], 2020. Available: https://heelkunde.nl/nieuws/nieuwsbericht?newsitemid=23658500 [Accessed 16 May 2022].
-
- Dutch Broadcasting Foundation . Healthcare authority: dozens of hospitals cancelled urgent operations because of corona [online], 2021. Available: https://nos.nl/artikel/2362513-zorgautoriteit-tientallen-ziekenhuizen-sc... [Accessed 12 Apr 2021].
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
