miR-29c-5p knockdown reduces inflammation and blood-brain barrier disruption by upregulating LRP6
- PMID: 35799601
- PMCID: PMC8864056
- DOI: 10.1515/med-2022-0438
miR-29c-5p knockdown reduces inflammation and blood-brain barrier disruption by upregulating LRP6
Abstract
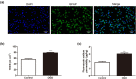
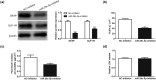
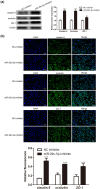
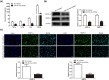
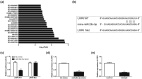
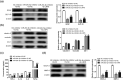
Blood-brain barrier participates in the pathological process of ischemic stroke. MicroRNA-29c-5p was highly expressed in clinical samples from patients with ischemic stroke. In this study, oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD) treatment of astrocytes enhanced the permeability of brain microvascular endothelial cells (BMECs), and the miR-29c-5p expression was elevated in clinical samples from patients with ischemic stroke. For the function of miR-29c-5p in ischemic stroke, the miR-29c-5p knockdown decreased the permeability and the tight junction protein (TJP) destruction of BMECs and ameliorated the inflammation induced by OGD-treated astrocytes. Mechanistically, miR-29c-5p interacted with lipoprotein receptor-related protein 6 (LRP6) and negatively regulated the LRP6 expression in astrocytes. Moreover, the rescue assays indicated that the interference with miR-29c-5p ameliorated the TJP destruction of BMECs and inflammation caused by OGD-treated astrocytes by increasing the LRP6 expression. Together, miR-29c-5p knockdown decreased the high permeability and the TJP destruction of BMECs and ameliorated the inflammation induced by OGD-treated astrocytes by elevating LRP6 expression.
Keywords: astrocytes; blood–brain barrier; brain microvascular endothelial cells; ischemic stroke; miRNA.
© 2022 Qijun Dai et al., published by De Gruyter.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abdullahi W, Tripathi D, Ronaldson PT. Blood-brain barrier dysfunction in ischemic stroke: targeting tight junctions and transporters for vascular protection. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2018;315(3):C343–56. - PMC - PubMed
- Abdullahi W, Tripathi D, Ronaldson PT. Blood-brain barrier dysfunction in ischemic stroke: targeting tight junctions and transporters for vascular protection. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2018;315(3):C343–56. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Schoknecht K, David Y, Heinemann U. The blood-brain barrier-gatekeeper to neuronal homeostasis: clinical implications in the setting of stroke. SemCell Developmental Biol. 2015;38:35–42. - PubMed
- Schoknecht K, David Y, Heinemann U. The blood-brain barrier-gatekeeper to neuronal homeostasis: clinical implications in the setting of stroke. SemCell Developmental Biol. 2015;38:35–42. - PubMed
-
- Shah K, Abbruscato T. The role of blood-brain barrier transporters in pathophysiology and pharmacotherapy of stroke. Curr Pharm Des. 2014;20(10):1510–22. - PubMed
- Shah K, Abbruscato T. The role of blood-brain barrier transporters in pathophysiology and pharmacotherapy of stroke. Curr Pharm Des. 2014;20(10):1510–22. - PubMed
-
- Jiang X, Andjelkovic AV, Zhu L, Yang T, Bennett MVL, Chen J, et al. Blood-brain barrier dysfunction and recovery after ischemic stroke. Prog Neurobiol. 2018;163–164:144–71. - PMC - PubMed
- Jiang X, Andjelkovic AV, Zhu L, Yang T, Bennett MVL, Chen J. et al. Blood-brain barrier dysfunction and recovery after ischemic stroke. Prog Neurobiol. 2018;163–164:144–71. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
