Effect of Kvass on Improving Functional Dyspepsia in Rats
- PMID: 35799630
- PMCID: PMC9256358
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/5169892
Effect of Kvass on Improving Functional Dyspepsia in Rats
Abstract
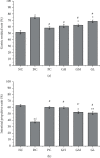
Functional dyspepsia (FD) is a common digestive system disease, and probiotics in the treatment of FD have a good curative effect. Patients with gastrointestinal diseases often show a poor response to traditional drug treatments and suffer from adverse reactions. Kvass can be used as a functional drink without side effects to improve the symptoms of FD patients. The results showed that compared with those of the model group, the body weight and food intake of the treatment group were significantly increased (P < 0.05), and the gastric residual rate of the treatment group was significantly decreased (P < 0.05); the amount of pepsin in the treatment group was significantly higher than that in the model group (P < 0.05); a high dose of Kvass could increase the contents of ghrelin, motilin (MTL), and gastrin (GAS) in the plasma and decrease the contents of vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) in the plasma; the contents of ghrelin, MTL, and GAS in the gastric antrum were also increased in the high-dose group. Kvass beverage can significantly improve the gastrointestinal function of rats, which may be because it can improve the contents of ghrelin, MTL, GAS, and VIP in both the serum and gastric antrum by regulating the expression of short-chain fatty acids in the colon.
Copyright © 2022 Zhanmei Shao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Osipova M. V. Use of clarifying agents in technological process of kvass production. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science . 2020;613(1, article 012100) doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/613/1/012100. - DOI
-
- Lucas W., Matthias C., Karlien G., et al. 464 Efficacy and safety of spore-forming probiotics in functional dyspepsia: a randomized placebo-controlled trial. Gastroenterology . 2021;160(6) doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(21)00969-0. - DOI
-
- Lorenzo D., Gabriele M., Dario P., Luigi P., Giuseppe M. Evaluation of main functional dyspepsia symptoms after probiotic administration in patients receiving conventional pharmacological therapies. Journal of International Medical Research . 2021;49(1) doi: 10.1177/0300060520982657. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Agah S., Akbari A., Heshmati J., et al. Systematic review with meta-analysis: effects of probiotic supplementation on symptoms in functional dyspepsia. Journal of Functional Foods . 2020;68:p. 103902. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2020.103902. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

