A SARS-Cov-2 sensor based on upconversion nanoparticles and graphene oxide
- PMID: 35799935
- PMCID: PMC9215703
- DOI: 10.1039/d2ra03599e
A SARS-Cov-2 sensor based on upconversion nanoparticles and graphene oxide
Abstract
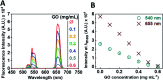
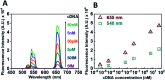
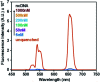
Since the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic, there has been an increased need for the development of novel diagnostic solutions that can accurately and rapidly detect SARS-CoV-2 infection. In this work, we demonstrate the targeting of viral oligonucleotide markers within minutes without the requirement of a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification step via the use of oligonucleotide-coated upconversion nanoparticles (UCNPs) and graphene oxide (GO).
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Fabrication of chitosan-coated mixed spinel ferrite integrated with graphene oxide (GO) for magnetic extraction of viral RNA for potential detection of SARS-CoV-2.Appl Phys A Mater Sci Process. 2021;127(12):960. doi: 10.1007/s00339-021-05067-7. Epub 2021 Nov 27. Appl Phys A Mater Sci Process. 2021. PMID: 34866806 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of upconversion nanoparticles on polymerase chain reaction.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 5;8(9):e73408. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0073408. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24039935 Free PMC article.
-
A novel ADA-coated UCNPs@NB sensing platform combined with nucleic acid amplification for rapid detection of Escherichia coli.Anal Chim Acta. 2023 Jan 25;1239:340751. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2022.340751. Epub 2022 Dec 27. Anal Chim Acta. 2023. PMID: 36628739
-
Designing next generation of photon upconversion: Recent advances in organic triplet-triplet annihilation upconversion nanoparticles.Biomaterials. 2019 May;201:77-86. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2019.02.008. Epub 2019 Feb 12. Biomaterials. 2019. PMID: 30802685 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Recent Update on Advanced Molecular Diagnostic Techniques for COVID-19 Pandemic: An Overview.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 14;12:732756. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.732756. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34970254 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Digital and Analog Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein via an Upconversion-Linked Immunosorbent Assay.Anal Chem. 2023 Mar 14;95(10):4753-4759. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.2c05670. Epub 2023 Feb 27. Anal Chem. 2023. PMID: 36916131 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging trends in point-of-care biosensing strategies for molecular architectures and antibodies of SARS-CoV-2.Biosens Bioelectron X. 2023 May;13:100324. doi: 10.1016/j.biosx.2023.100324. Epub 2023 Feb 21. Biosens Bioelectron X. 2023. PMID: 36844889 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plasmon Modulated Upconversion Biosensors.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Feb 22;13(3):306. doi: 10.3390/bios13030306. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36979518 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanotechnology-Assisted Biosensors for the Detection of Viral Nucleic Acids: An Overview.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Jan 30;13(2):208. doi: 10.3390/bios13020208. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36831973 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances of Representative Optical Biosensors for Rapid and Sensitive Diagnostics of SARS-CoV-2.Biosensors (Basel). 2022 Oct 12;12(10):862. doi: 10.3390/bios12100862. Biosensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36291001 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

