Correlation between the Expression of VEGF and Ki67 and Lymph Node Metastasis in Non-small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 35800006
- PMCID: PMC9256412
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/9693746
Correlation between the Expression of VEGF and Ki67 and Lymph Node Metastasis in Non-small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Correlation between the Expression of VEGF and Ki67 and Lymph Node Metastasis in Non-small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023 Dec 6;2023:9894125. doi: 10.1155/2023/9894125. eCollection 2023. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023. PMID: 38093895 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Lymph node metastasis is the most common and important way of metastasis in NSCLC and is also the most important factor affecting lung cancer stage and prognosis. It is very important to analyze the relationship between the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and Ki67 and lymph node metastasis (LNM) in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Methods: We searched the PubMed, EMBASE, and Cochrane Library and conducted meta-analyses using the R meta-package. Relative risk (RR) with a 95% confidence interval (95% CI) was the main indicator.
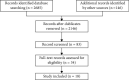
Results: Totally, 18 studies were considered eligible, with 4521 patients, including 1518 LNM-positive patients and 3033 LNM-negative patients. The incidence of LNM in Ki67-negative patients was lower than that in Ki67-positive patients (RR = 0.66, 95% CI: 0.44, 0.98). The incidence of LNM in VEGF-A-negative patients was lower than that in VEGF-A-positive patients (RR = 0.64, 95% CI: 0.49, 0.83). The incidence of LNM in VEGF-C negative patients was lower than that in VEGF-C positive patients (RR = 0.68, 95% CI: 0.53, 0.88). The incidence of LNM in VEGF-D negative and positive patients were of no significant differences (RR = 0.84, 95% CI: 0.61, 1.14).
Conclusion: The high expression of Ki67, VEGF-A, and VEGF-C significantly increases the risk of lymph node metastasis in NSCLC, while the VEGF-D expression has no correlation with lymph node metastasis. The expression levels of Ki67, VEGF-A, and VEGF-C show a good potential for lymph node metastasis prediction.
Copyright © 2022 Dong Wei et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Association between VEGF-A, C and D expression and lymph node involvement in breast cancer: a meta-analysis.Int J Biol Markers. 2016 Jul 30;31(3):e235-44. doi: 10.5301/jbm.5000198. Int J Biol Markers. 2016. PMID: 26954069
-
Association between vascular endothelial growth factor expression and lymph node metastasis in cervical cancer: A meta-analysis.J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2016 Oct;42(10):1310-1316. doi: 10.1111/jog.13064. Epub 2016 Jun 23. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2016. PMID: 27334572
-
Phosphatase and tensin homolog protein may be linked to lymph node metastasis and tumor node metastasis staging in nonsmall cell lung cancer.J Cancer Res Ther. 2018;14(Supplement):S138-S144. doi: 10.4103/0973-1482.165865. J Cancer Res Ther. 2018. PMID: 29578164
-
Risk factors for lymph node metastasis in T1 esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis.World J Gastroenterol. 2021 Feb 28;27(8):737-750. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i8.737. World J Gastroenterol. 2021. PMID: 33716451 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy on Lymph Node Metastasis of FIGO Stage IB1-IIB Cervical Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Oncol. 2020 Nov 5;10:570258. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.570258. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33251136 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Does the Expression of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) and Bcl-2 Have a Prognostic Significance in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer?Healthcare (Basel). 2023 Jan 18;11(3):292. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11030292. Healthcare (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36766867 Free PMC article.
-
Factors correlating the expression of PD-L1.BMC Cancer. 2024 May 25;24(1):642. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12400-9. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38796458 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory Effects of SLC7A2-CPB2 on Lymphangiogenesis: A New Approach to Suppress Lymphatic Metastasis in HNSCC.Cancer Med. 2024 Oct;13(19):e70273. doi: 10.1002/cam4.70273. Cancer Med. 2024. PMID: 39382373 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophils in tumor- and inflammation-induced lymphangiogenesis.Int J Biol Sci. 2025 Feb 26;21(5):2223-2234. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.103458. eCollection 2025. Int J Biol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40083688 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic role of tumor microenvironment and immune- and autophagy-related genes in colorectal adenocarcinoma.Transl Cancer Res. 2025 May 30;14(5):2835-2857. doi: 10.21037/tcr-24-1708. Epub 2025 May 27. Transl Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40530112 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

