Computed Tomography Image under Artificial Intelligence Algorithm to Evaluate the Nursing and Treatment Effect of Pemetrexed Combined Platinum-Based Chemotherapy on Elderly Lung Cancer
- PMID: 35800237
- PMCID: PMC9192264
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/2574451
Computed Tomography Image under Artificial Intelligence Algorithm to Evaluate the Nursing and Treatment Effect of Pemetrexed Combined Platinum-Based Chemotherapy on Elderly Lung Cancer
Abstract
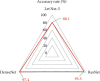
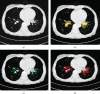
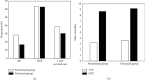
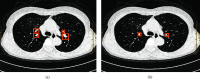
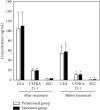
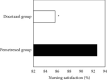
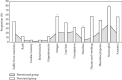
This study was to evaluate the clinical efficacy of pemetrexed combined with platinum-based chemotherapy in the treatment of elderly lung cancer using electronic computed tomography (CT) images based on artificial intelligence algorithms. In this study, 80 elderly patients with lung cancer treated were selected and randomly divided into two groups: patients treated with pemetrexed combined with cisplatin were included in the pemetrexed group and patients treated with docetaxel combined with cisplatin were included in the docetaxel group, with 40 cases in each group. The DenseNet network was compared with the Let Net-5 and ResNet model and applied to the CT images of 80 elderly patients with lung cancer. The diagnosis accuracy of the DenseNet network (97.4%) was higher than that of the Let Net-5 network (80.1%) and ResNet model (95.5%). Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), cytokeratin fragment antigen 21-1 (CYFRA 21-1), and squamous cell-associated antigen (SCC) after chemotherapy in the pemetrexed group and docetaxel group were all lower than those before chemotherapy, showing statistically obvious differences (P < 0.05). The satisfaction degree of nursing care in the pemetrexed group (92.67%) was significantly higher than that in the docetaxel group (85.62%), and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). Adverse reactions such as fatigue, diarrhea, and neutrophils in the pemetrexed group were lower than those in the docetaxel group, and the difference was statistically great (P < 0.05). The DenseNet convolutional neural network has high diagnostic accuracy; methotrexate combined with platinum chemotherapy can improve the chemotherapy effect in elderly patients with lung cancer, with low degree of adverse reactions and good overall tolerance, which can be used as the first-line treatment for elderly patients with lung cancer.
Copyright © 2022 Qing Gu and Shu'e Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
CYFRA 21-1 as a Predictive Marker for Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Treated with Pemetrexed-based Chemotherapy.Anticancer Res. 2017 Feb;37(2):935-939. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.11402. Anticancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28179355
-
Salvage treatment with irinotecan/cisplatin versus pemetrexed/cisplatin in patients with non-small cell lung cancer pre-treated with a non-platinum-based regimen in the first-line setting: a randomized phase II study of the Hellenic Oncology Research Group (HORG).Clin Transl Oncol. 2017 Mar;19(3):317-325. doi: 10.1007/s12094-016-1532-y. Epub 2016 Aug 4. Clin Transl Oncol. 2017. PMID: 27492015 Clinical Trial.
-
Customized Adjuvant Chemotherapy Based on Biomarker Examination May Improve Survival of Patients Completely Resected for Non-small-cell Lung Cancer.Anticancer Res. 2017 May;37(5):2501-2507. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.11591. Anticancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28476819
-
Pemetrexed for the maintenance treatment of locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2010 Oct;14(Suppl. 2):33-9. doi: 10.3310/hta14suppl2/05. Health Technol Assess. 2010. PMID: 21047489 Review.
-
Second-line chemotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer: recent data with pemetrexed.Clin Lung Cancer. 2004 Apr;5 Suppl 2:S75-9. doi: 10.3816/clc.2004.s.007. Clin Lung Cancer. 2004. PMID: 15117429 Review.
Cited by
-
Artificial Intelligence in Thoracic Surgery: A Review Bridging Innovation and Clinical Practice for the Next Generation of Surgical Care.J Clin Med. 2025 Apr 16;14(8):2729. doi: 10.3390/jcm14082729. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40283559 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Thorough Review of the Clinical Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Lung Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Mar 4;17(5):882. doi: 10.3390/cancers17050882. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40075729 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Papadimitrakopoulou V. A., Mok T. S., Han J. Y., et al. Osimertinib versus platinum-pemetrexed for patients with EGFR T790M advanced NSCLC and progression on a prior EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitor: AURA3 overall survival analysis. Annals of Oncology . 2020 November;31(11):1536–1544. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2020.08.2100. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Garassino M. C., Gadgeel S., Esteban E., et al. Patient-reported outcomes following pembrolizumab or placebo plus pemetrexed and platinum in patients with previously untreated, metastatic, non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer (KEYNOTE-189): a multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. The Lancet Oncology . 2020 March;21(3):387–397. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30801-0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Papadimitrakopoulou V. A., Han J. Y., Ahn M. J., et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor mutation analysis in tissue and plasma from the AURA3 trial: osimertinib versus platinum-pemetrexed for T790M mutation-positive advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer . 2020 January 15;126(2):373–380. doi: 10.1002/cncr.32503. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
