Immediate-release tofacitinib reduces insulin resistance in non-diabetic active rheumatoid arthritis patients: A single-center retrospective study
- PMID: 35800413
- PMCID: PMC9210542
- DOI: 10.4239/wjd.v13.i6.454
Immediate-release tofacitinib reduces insulin resistance in non-diabetic active rheumatoid arthritis patients: A single-center retrospective study
Abstract
Background: An increased risk of insulin resistance (IR) has been identified in rheumatoid arthritis (RA), a chronic inflammatory disorder with elevated levels of pathogenic cytokines. Biologics targeting proinflammatory cytokines can control the disease and improve insulin sensitivity in RA. Although Janus kinase (JAK) signaling can regulate cytokine receptors and participate in RA pathogenesis, it remains to be elucidated whether there is a reduction of IR in such patients under JAK inhibitor (JAKi) therapy.
Aim: To study the effect of JAKi treatment on the reduction of IR in RA patients with active disease.
Methods: A retrospective study was carried out from April 1, 2017 to March 31, 2021 in a population of non-diabetic patients with active RA who were undergoing tofacitinib (TOF) therapy with 5 mg twice-daily immediate-release formulation.
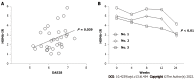
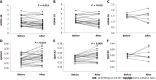
Results: Fifty-six RA patients, aged 30 years to 75 years (mean ± SD: 52.3 ± 11.1) with disease activity score 28 values ranging from 4.54 to 7.37 (5.82 ± 0.74), were classified into high-IR (> 2.0) and low-IR (≤ 2.0) groups based on their baseline homeostatic model assessment (HOMA)-IR levels. They had no previous exposure to JAKi, and received TOF therapy for no less than 6 mo. In 30 patients who were naïve to biologics, after a 24-week therapeutic period, the high-IR group showed reduced HOMA-IR levels (3.331 ± 1.036 vs 2.292 ± 0.707, P < 0.001). In another 26 patients who were exposed to tumor necrosis factor-α or interleukin-6 blockers, the high-IR group, despite having achieved a decrease but with lower magnitude than in naïve patients, showed reduced HOMA-IR levels (2.924 ± 0.790 vs 2.545 ± 1.080, P = 0.018).
Conclusion: In this retrospective study, reduced IR was achieved in non-diabetic active RA patients following 24 wk of TOF therapy.
Keywords: Diabetes mellitus; Insulin resistance; Janus kinase inhibitor; Rheumatoid arthritis; Tofacitinib.
©The Author(s) 2022. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All the authors report no relevant conflicts of interest for this article.
Figures

References
-
- Khodabandehloo H, Gorgani-Firuzjaee S, Panahi G, Meshkani R. Molecular and cellular mechanisms linking inflammation to insulin resistance and β-cell dysfunction. Transl Res. 2016;167:228–256. - PubMed
-
- Nicolau J, Lequerré T, Bacquet H, Vittecoq O. Rheumatoid arthritis, insulin resistance, and diabetes. Joint Bone Spine. 2017;84:411–416. - PubMed
-
- Kanety H, Feinstein R, Papa MZ, Hemi R, Karasik A. Tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1). Possible mechanism for suppression of insulin-stimulated tyrosine phosphorylation of IRS-1. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:23780–23784. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

