National perspective on hospital readmissions following adrenalectomy
- PMID: 35800745
- PMCID: PMC9253180
- DOI: 10.21037/gs-22-18
National perspective on hospital readmissions following adrenalectomy
Abstract
Background: Examining risk factors of readmission in adrenalectomy patients and estimated the cost burden of unplanned readmission on the United States' healthcare system.
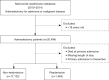
Methods: According to the Nationwide Readmission Database, 20,494 patients underwent adrenalectomy between 2010-2014. Demographics, comorbidities, clinical data, length of stay (LOS), annual case volume, and discharge disposition of 30- and 90-day readmission cohorts were compared to the non-readmitted cohort.
Results: A total of 1,463 (7.9%) and 1,959 (12.7%) adrenalectomy patients were readmitted at 30 and 90 days after discharge, respectively. Prolonged initial hospital stays [odds ratio (OR) =1.93; 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.63-2.27] and postoperative complications (OR =4.91; 95% CI: 1.98-12.16) were associated with a higher risk of readmission. Complications were significantly more frequent in patients with a primary or secondary malignancy (OR =1.42; 95% CI: 1.23-1.64) and in patients undergoing a procedure at a low adrenalectomy volume hospital [hazard ratio (HR) =0.75; 95% CI: 0.62-0.91; P=0.003]. Readmission extended overall LOS by an average of 2.06 days, costing an additional $18,529.49 per admission.
Conclusions: Readmission adds significantly to the burden of disease after adrenalectomy. Understanding contributing factors may identify strategies to reduce readmissions and improve healthcare for patients.
Keywords: Adrenalectomy; complication rate; healthcare cost; length of stay (LOS); readmission rate.
2022 Gland Surgery. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://gs.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/gs-22-18/coif). EK serves as an Editor-in-Chief of Gland Surgery from May 2017 to April 2024. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


Comment in
-
Improving outcomes for patients following adrenal surgery: the importance of addressing unwarranted variation in surgical volumes.Gland Surg. 2022 Jul;11(7):1130-1132. doi: 10.21037/gs-22-336. Gland Surg. 2022. PMID: 35935560 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Factors contributing to readmissions after laparoscopic adrenalectomy.Gland Surg. 2022 Jul;11(7):1133-1135. doi: 10.21037/gs-22-314. Gland Surg. 2022. PMID: 35935567 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
