Blueprints for measuring natural behavior
- PMID: 35800771
- PMCID: PMC9254349
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.104635
Blueprints for measuring natural behavior
Abstract
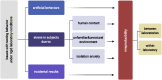
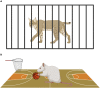
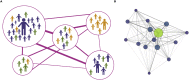
Until recently laboratory tasks for studying behavior were highly artificial, simplified, and designed without consideration for the environmental or social context. Although such an approach offers good control over behavior, it does not allow for researching either voluntary responses or individual differences. Importantly for neuroscience studies, the activity of the neural circuits involved in producing unnatural, artificial behavior is variable and hard to predict. In addition, different ensembles may be activated depending on the strategy the animal adopts to deal with the spurious problem. Thus, artificial and simplified tasks based on responses, which do not occur spontaneously entail problems with modeling behavioral impairments and underlying brain deficits. To develop valid models of human disorders we need to test spontaneous behaviors consistently engaging well-defined, evolutionarily conserved neuronal circuits. Such research focuses on behavioral patterns relevant for surviving and thriving under varying environmental conditions, which also enable high reproducibility across different testing settings.
Keywords: Behavioral neuroscience; Biological sciences; Neuroscience.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests in relation to the work described.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Action detection using a neural network elucidates the genetics of mouse grooming behavior.Elife. 2021 Mar 17;10:e63207. doi: 10.7554/eLife.63207. Elife. 2021. PMID: 33729153 Free PMC article.
-
Neural Circuits for Social Cognition: Implications for Autism.Neuroscience. 2018 Feb 1;370:148-162. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2017.07.013. Epub 2017 Jul 17. Neuroscience. 2018. PMID: 28729065 Review.
-
Infusing neuroscience into the study and prevention of drug misuse and co-occurring aggressive behavior.Subst Use Misuse. 2009;44(9-10):1204-35. doi: 10.1080/10826080902959975. Subst Use Misuse. 2009. PMID: 19938915 Review.
-
The neurobiology of offensive aggression: Revealing a modular view.Physiol Behav. 2015 Jul 1;146:111-27. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2015.04.040. Physiol Behav. 2015. PMID: 26066717
-
Intrinsic excitability mechanisms of neuronal ensemble formation.Elife. 2022 May 4;11:e77470. doi: 10.7554/eLife.77470. Elife. 2022. PMID: 35506662 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Seminatural environments for rodent behavioral testing: a representative design improving animal welfare and enhancing replicability.Front Behav Neurosci. 2023 Jun 22;17:1192213. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2023.1192213. eCollection 2023. Front Behav Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37424748 Free PMC article.
-
Information sharing within a social network is key to behavioral flexibility-Lessons from mice tested under seminaturalistic conditions.Sci Adv. 2025 Jan 3;11(1):eadm7255. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adm7255. Epub 2025 Jan 3. Sci Adv. 2025. PMID: 39752499 Free PMC article.
-
Scale-Free Chaos in the 2D Harmonically Confined Vicsek Model.Entropy (Basel). 2023 Dec 11;25(12):1644. doi: 10.3390/e25121644. Entropy (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38136524 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term tracking of social structure in groups of rats.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 1;14(1):22857. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-72437-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39353967 Free PMC article.
-
IntelliCage: the development and perspectives of a mouse- and user-friendly automated behavioral test system.Front Behav Neurosci. 2024 Jan 3;17:1270538. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2023.1270538. eCollection 2023. Front Behav Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38235003 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alboni S., van Dijk R.M., Poggini S., Milior G., Perrotta M., Drenth T., Brunello N., Wolfer D.P., Limatola C., Amrein I., et al. Fluoxetine effects on molecular, cellular and behavioral endophenotypes of depression are driven by the living environment. Mol. Psychiatry. 2017;22:552–561. doi: 10.1038/mp.2015.142. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

