Definition and classification of acute-on-chronic liver diseases
- PMID: 35801045
- PMCID: PMC9198886
- DOI: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i15.4717
Definition and classification of acute-on-chronic liver diseases
Abstract
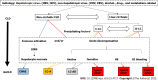
Patients with chronic liver diseases (CLDs) develop acute liver injury and/or acute decompensation under the attack of various precipitants and present with significantly elevated alanine aminotransferase and/or total bilirubin levels, liver failure, or acute decompensation of liver cirrhosis, which is called acute-on-CLD (AoCLD). AoCLD accounts for the majority of patients hospitalized in the Department of Hepatology or Infectious Diseases. AoCLD is complicated by various clinical types, the severity of the disease, and may pose a high risk of death. To date, the definition of AoCLD is still vague, and a consensus concept of the clinical classification is lacking. This review aimed to define the concept and clinical types of AoCLD based on related studies and the literature.
Keywords: Acute decompensation; Acute liver injury; Acute-on-chronic liver disease; Acute-on-chronic liver failure; Chronic liver disease.
©The Author(s) 2022. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Li M, Wang ZQ, Zhang L, Zheng H, Liu DW, Zhou MG. Burden of Cirrhosis and Other Chronic Liver Diseases Caused by Specific Etiologies in China, 1990-2016: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Biomed Environ Sci. 2020;33:1–10. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

