Ovarian Steroids Mediate Sex Differences in Alcohol Reward After Brain Injury in Mice
- PMID: 35801094
- PMCID: PMC9253769
- DOI: 10.3389/fnbeh.2022.907552
Ovarian Steroids Mediate Sex Differences in Alcohol Reward After Brain Injury in Mice
Abstract
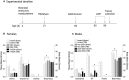
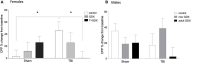
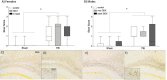
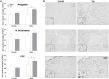
Intoxication is a leading risk factor for injury, and TBI increases the risk for later alcohol misuse, especially when the injury is sustained in childhood. Previously, we modeled this pattern in mice, wherein females injured at postnatal day 21 drank significantly more than uninjured females, while we did not see this effect in males. However, the biological underpinnings of this sex difference have remained elusive. In this study, we utilize this preclinical model and traditional endocrine manipulations to assess the effect of perinatal sex steroids on post-injury ethanol response. We found that perinatal androgen administration and adult ovariectomy prevented the development of conditioned place preference to ethanol in females, while there was not an effect of gonadectomy either developmental time point on the severity of axonal degeneration. Finally, although TBI increased the number of microglia in males, there was no corresponding effect of gonadectomy, which suggests that males exhibit prolonged neuroinflammation after brain injury irrespective of circulating sex steroids. Taken together, our results indicate a potential role for ovarian sex steroids in the development of greater alcohol preference after a juvenile TBI in female mice.
Keywords: alcohol; androgens; organizational effects; ovaries; sex steroids; traumatic brain injury.
Copyright © 2022 Oliverio, Fitzgerald, Velazquez-Cruz, Whitehead, Karelina and Weil.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Adams R. S., Larson M. J., Corrigan J. D., Horgan C. M., Williams T. V. (2012). Frequent Binge Drinking After Combat-Acquired Traumatic Brain Injury Among Active Duty Military Personnel With a Past Year Combat Deployment. J. Head Trauma Rehabil. 27 349–360. 10.1097/HTR.0b013e318268db94 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

