An Optimized Miniaturized Ultrasound Transducer for Transcranial Neuromodulation
- PMID: 35801172
- PMCID: PMC9253503
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2022.893108
An Optimized Miniaturized Ultrasound Transducer for Transcranial Neuromodulation
Abstract
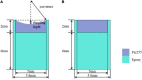
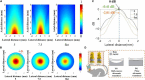
Transcranial ultrasound stimulation (TUS) is a young neuromodulation technology, which uses ultrasound to achieve non-invasive stimulation or inhibition of deep intracranial brain regions, with the advantages of non-invasive, deep penetration, and high resolution. It is widely considered to be one of the most promising techniques for probing brain function and treating brain diseases. In preclinical studies, developing miniaturized transducers to facilitate neuromodulation in freely moving small animals is critical for understanding the mechanism and exploring potential applications. In this article, a miniaturized transducer with a half-concave structure is proposed. Based on the finite element simulation models established by PZFlex software, several ultrasound transducers with different concave curvatures were designed and analyzed. Based on the simulation results, half-concave focused ultrasonic transducers with curvature radii of 5 mm and 7.5 mm were fabricated. Additionally, the emission acoustic fields of the ultrasonic transducers with different structures were characterized at their thickness resonance frequencies of 1 MHz using a multifunctional ultrasonic test platform built in the laboratory. To verify the practical ability for neuromodulation, different ultrasound transducers were used to induce muscle activity in mice. As a result, the stimulation success rates were (32 ± 10)%, (65 ± 8)%, and (84 ± 7)%, respectively, by using flat, #7, and #5 transducers, which shows the simulation and experimental results have a good agreement and that the miniaturized half-concave transducer could effectively converge the acoustic energy and achieve precise and effective ultrasonic neuromodulation.
Keywords: FEM simulation; converge acoustic energy; half-concave structure; neuromodulation; ultrasonic transducer.
Copyright © 2022 Hou, Wu, Fei, Qiu, Li, Sun, Zheng and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Simultaneous multi-target ultrasound neuromodulation in freely-moving mice based on a single-element ultrasound transducer.J Neural Eng. 2023 Jan 20;20(1). doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/acb104. J Neural Eng. 2023. PMID: 36608340
-
Miniature ultrasound ring array transducers for transcranial ultrasound neuromodulation of freely-moving small animals.Brain Stimul. 2019 Mar-Apr;12(2):251-255. doi: 10.1016/j.brs.2018.11.007. Epub 2018 Nov 17. Brain Stimul. 2019. PMID: 30503712
-
Capacitive Micromachined Ultrasonic Transducer (CMUT) ring array for transcranial ultrasound neuromodulation.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2018 Jul;2018:2675-2678. doi: 10.1109/EMBC.2018.8512731. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2018. PMID: 30440957
-
A practical guide to transcranial ultrasonic stimulation from the IFCN-endorsed ITRUSST consortium.Clin Neurophysiol. 2025 Mar;171:192-226. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2025.01.004. Epub 2025 Jan 28. Clin Neurophysiol. 2025. PMID: 39933226 Review.
-
Noninvasive intervention by transcranial ultrasound stimulation: Modulation of neural circuits and its clinical perspectives.Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2024 May;78(5):273-281. doi: 10.1111/pcn.13663. Epub 2024 Mar 20. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38505983 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic ultrasound: an innovative approach for targeting neurological disorders affecting the basal ganglia.Front Neuroanat. 2024 Oct 2;18:1469250. doi: 10.3389/fnana.2024.1469250. eCollection 2024. Front Neuroanat. 2024. PMID: 39417047 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Crew H., Huygens C., Young T., Fresnel A., Arago F. (1900). The Wave Theory Of Light. New York: American Book Company.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

