Hypertonic Solution in Severe COVID-19 Patient: A Potential Adjuvant Therapy
- PMID: 35801207
- PMCID: PMC9253300
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2022.917008
Hypertonic Solution in Severe COVID-19 Patient: A Potential Adjuvant Therapy
Abstract
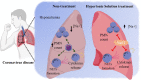
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) features hyper-inflammation, cytokine storm, neutrophil function changes, and sodium chloride (NaCl) homeostasis disruption, while the treatment with NaCl hypertonic solutions (HS) controls electrolytic body homeostasis and cell functions. HS treatment is a simple, popular, economic, and feasible therapy to regulate leukocyte function with a robust anti-inflammatory effect in many inflammatory diseases. The purpose of this narrative review is to highlight the knowledge on the use of HS approaches against viral infection over the past years and to describe the mechanisms involved in the release of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) and production of cytokine in severe lung diseases, such as COVID-19. We reported the consequences of hyponatremia in COVID-19 patients, and the immunomodulatory effects of HS, either in vitro or in vivo. We also described the relationship between electrolyte disturbances and COVID-19 infection. Although there is still a lack of clinical trials, hypertonic NaCl solutions have marked effects on neutrophil function and NETs formation, emerging as a promising adjuvant therapy in COVID-19.
Keywords: NETosis; NETs; NaCl; coronavirus; immune system; leukocytes; neutrophils.
Copyright © 2022 Gennari-Felipe, Borges, Dermargos, Weimann, Curi, Pithon-Curi and Hatanaka.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous