Integration of various protein similarities using random forest technique to infer augmented drug-protein matrix for enhancing drug-disease association prediction
- PMID: 35801312
- PMCID: PMC10358641
- DOI: 10.1177/00368504221109215
Integration of various protein similarities using random forest technique to infer augmented drug-protein matrix for enhancing drug-disease association prediction
Abstract
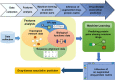
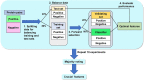
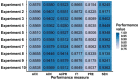
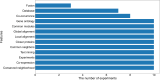
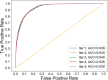
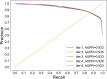
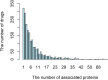
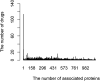
Identifying new therapeutic indications for existing drugs is a major challenge in drug repositioning. Most computational drug repositioning methods focus on known targets. Analyzing multiple aspects of various protein associations provides an opportunity to discover underlying drug-associated proteins that can be used to improve the performance of the drug repositioning approaches. In this study, machine learning models were developed based on the similarities of diversified biological features, including protein interaction, topological network, sequence alignment, and biological function to predict protein pairs associating with the same drugs. The crucial set of features was identified, and the high performances of protein pair predictions were achieved with an area under the curve (AUC) value of more than 93%. Based on drug chemical structures, the drug similarity levels of the promising protein pairs were used to quantify the inferred drug-associated proteins. Furthermore, these proteins were employed to establish an augmented drug-protein matrix to enhance the efficiency of three existing drug repositioning techniques: a similarity constrained matrix factorization for the drug-disease associations (SCMFDD), an ensemble meta-paths and singular value decomposition (EMP-SVD) model, and a topology similarity and singular value decomposition (TS-SVD) technique. The results showed that the augmented matrix helped to improve the performance up to 4% more in comparison to the original matrix for SCMFDD and EMP-SVD, and about 1% more for TS-SVD. In summary, inferring new protein pairs related to the same drugs increase the opportunity to reveal missing drug-associated proteins that are important for drug development via the drug repositioning technique.
Keywords: Protein-protein interaction network; drug repositioning; drug repurposing; drug-protein association; machine learning.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prediction of drug-disease associations based on ensemble meta paths and singular value decomposition.BMC Bioinformatics. 2019 Mar 29;20(Suppl 3):134. doi: 10.1186/s12859-019-2644-5. BMC Bioinformatics. 2019. PMID: 30925858 Free PMC article.
-
Link Prediction Only With Interaction Data and its Application on Drug Repositioning.IEEE Trans Nanobioscience. 2020 Jul;19(3):547-555. doi: 10.1109/TNB.2020.2990291. Epub 2020 Apr 24. IEEE Trans Nanobioscience. 2020. PMID: 32340956
-
Computational drug repositioning based on multi-similarities bilinear matrix factorization.Brief Bioinform. 2021 Jul 20;22(4):bbaa267. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbaa267. Brief Bioinform. 2021. PMID: 33147616
-
Drug-Disease Association Prediction Using Heterogeneous Networks for Computational Drug Repositioning.Biomolecules. 2022 Oct 17;12(10):1497. doi: 10.3390/biom12101497. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36291706 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Using Drug Expression Profiles and Machine Learning Approach for Drug Repurposing.Methods Mol Biol. 2019;1903:219-237. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-8955-3_13. Methods Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30547445 Review.
Cited by
-
A Drug Similarity-Based Bayesian Method for Early Adverse Drug Event Detection.Drug Saf. 2025 Aug;48(8):923-931. doi: 10.1007/s40264-025-01545-6. Epub 2025 Apr 22. Drug Saf. 2025. PMID: 40261506 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blockeel H, Kersting K, Nijssen S, et al.Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases. 2013.
-
- Ashburn TT, Thor KB. Drug repositioning: identifying and developing new uses for existing drugs. Nat Rev Drug Discovery 2004; 3: 673–683. - PubMed
-
- Sleigh SH, Barton CL. Repurposing strategies for therapeutics. Pharmaceut Med 2010; 24: 151–159.
-
- Roses AD. Pharmacogenetics in drug discovery and development: a translational perspective. Nat Rev Drug Discovery 2008; 7: 807–817. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

