Innovative pulmonary targeting of terbutaline sulfate-laded novasomes for non-invasive tackling of asthma: statistical optimization and comparative in vitro/ in vivo evaluation
- PMID: 35801404
- PMCID: PMC9272939
- DOI: 10.1080/10717544.2022.2092236
Innovative pulmonary targeting of terbutaline sulfate-laded novasomes for non-invasive tackling of asthma: statistical optimization and comparative in vitro/ in vivo evaluation
Abstract
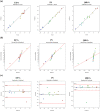
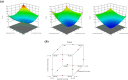
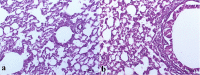
Asthma represents a globally serious non-communicable ailment with significant public health outcomes for both pediatrics and adults triggering vast morbidity and fatality in critical cases. The β2-adrenoceptor agonist, terbutaline sulfate (TBN), is harnessed as a bronchodilator for monitoring asthma noising symptoms. Nevertheless, the hepatic first-pass metabolism correlated with TBN oral administration mitigates its clinical performance. Likewise, the regimens of inhaled TBN dosage forms restrict its exploitation. Consequently, this work is concerned with the assimilation of TBN into a novel non-phospholipid nanovesicular paradigm termed novasomes (NVS) for direct and effective TBN pulmonary targeting. TBN-NVS were tailored based on the thin film hydration method and Box-Behnken design was applied to statistically optimize the formulation variables. Also, the aerodynamic pattern of the optimal TBN-NVS was explored via cascade impaction. Moreover, comparative pharmacokinetic studies were conducted using a rat model. TBN elicited encapsulation efficiency as high as 70%. The optimized TBN-NVS formulation disclosed an average nano-size of 223.89 nm, ζ potential of -31.17 mV and a sustained drug release up to 24 h. Additionally, it manifested snowballed in vitro lung deposition behavior in cascade impactor with a fine particle fraction of 86.44%. In vivo histopathological studies verified safety of intratracheally-administered TBN-NVS. The pharmacokinetic studies divulged 3.88-fold accentuation in TBN bioavailability from the optimum TBN-NVS versus the oral TBN solution. Concisely, the results proposed that NVS are an auspicious nanovector for TBN pulmonary delivery with integral curbing of the disease owing to target specificity.
Keywords: Box-Behnken design; Bronchial asthma; novasomes; pharmacokinetics; pulmonary targeting; terbutaline sulfate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Abd-Elal RM, Shamma RN, Rashed HM, Bendas E. (2016). Trans-nasal zolmitriptan novasomes: in-vitro preparation, optimization and in-vivo evaluation of brain targeting efficiency. Drug Deliv. 23:3374–86. - PubMed
-
- Abdelbary AA, AbouGhaly MH. (2015). Design and optimization of topical methotrexate loaded niosomes for enhanced management of psoriasis: application of Box–Behnken design, in-vitro evaluation and in-vivo skin deposition study. Int J Pharm 485:235–43. - PubMed
-
- Abdelrahim ME, Plant P, Chrystyn H. (2010). In-vitro characterisation of the nebulised dose during non-invasive ventilation. J Pharm Pharmacol 62:966–72. - PubMed
-
- Aboud HM, Ali AA, El-Menshawe SF, Elbary AA. (2016). Nanotransfersomes of carvedilol for intranasal delivery: formulation, characterization and in vivo evaluation. Drug Deliv 23:2471–81. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
