Anti-breast cancer sinomenine derivatives via mechanisms of apoptosis induction and metastasis reduction
- PMID: 35801430
- PMCID: PMC9272937
- DOI: 10.1080/14756366.2022.2096020
Anti-breast cancer sinomenine derivatives via mechanisms of apoptosis induction and metastasis reduction
Abstract
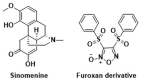
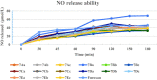
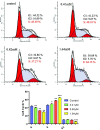
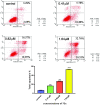
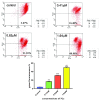
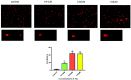
Sinomenine, a morphinane-type isoquinoline-derived alkaloid, was first isolated from stems and roots of Sinomenium diversifolius (Miq.) in 1920. Later discovery by researchers confirmed various essential biological efficacy sinomenine exerted in vitro and in vivo. In this study, a series of 15 sinomenine/furoxan hybrid compounds were designed and synthesised in search of a TNBC drug candidate. Some of the target compounds exhibited strong antiproliferative activities against cancer cell lines, especially for TNBC cells, compared to positive controls. Among them, hybrid 7Cc exerted superior cytotoxic effects on cancer cell lines with exceptionally low IC50 (0.82 μM) against MDA-MB-231 cells with the highest safety index score. Further studies in mechanism displayed that 7Cc could induce an S phase cell cycle arrest, stimulate apoptosis in MDA-MB-231 cells, disrupt mitochondrial membrane potential and exert a genotoxic effect on DNA in cancer cells. In addition, 7Cc also notably inhibited MDA-MB-231 cells in both migration, invasion and adhesion.
Keywords: Sinomenine; apoptosis; breast cancer; furoxan.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures

References
-
- International Agency for Research on Cancer, Global Cancer Observatory. Available from: https://gco.iarc.fr/today/home.
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 2015;65:87–105. - PubMed
-
- Rebecca LS, Kimberly DM, Fuchs HE, Ahmedin J.. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin 2022;65:87–108.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
