Anti‑oncogenic and pro‑myogenic action of the MKK6/p38/AKT axis induced by targeting MEK/ERK in embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma
- PMID: 35801577
- PMCID: PMC9350981
- DOI: 10.3892/or.2022.8363
Anti‑oncogenic and pro‑myogenic action of the MKK6/p38/AKT axis induced by targeting MEK/ERK in embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma
Abstract
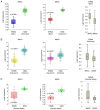
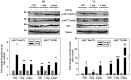
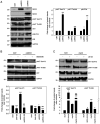
Insights into the molecular and cellular biology of embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma (ERMS), an aggressive paediatric tumour, are required in order to identify new targets for novel treatments that may benefit patients with this disease. The present study examined the functional effects of MKK3 and MKK6, two upstream kinases of p38, and found that the ectopic expression of MKK6 led to rapid p38 activation and the myogenic differentiation of ERMS cells, whereas MKK3 failed to induce differentiation, while maintaining the proliferation state. Myogenin and myosin heavy chain were induced in MKK6‑overexpressing ERMS cells and were inhibited by the p38 inhibitor, SB203580. The expression of Myc and ERK‑PO4 increased under the effect of SB203580, whereas it decreased in MKK6‑overexpressing cells. AKT activation was part of the myogenic program triggered by MKK6 overexpression alone. To the best of our knowledge, the present study demonstrates, for the first time, that the endogenous MKK6 pathway may be recovered by MEK/ERK inhibition (U0126 and trametinib) and that it concomitantly induces the reversal of the oncogenic pattern and the induction of the myogenic differentiation of ERMS cell lines. The effects of MEK/ERK inhibitors markedly increase the potential clinical applications in ERMS, particularly on account of the MEK inhibitor‑induced early MKK6/p38 axis activation and of their anti‑oncogenic effects. The findings presented herein lend further support to the antitumour effects of MKK6; MKK6 may thus represent a novel target for advanced personalised treatments against ERMS.
Keywords: MEK/ERK inhibitors; MKK6; Myc; embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma; p38.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures







References
-
- Shern JF, Chen L, Chmielecki J, Wei JS, Patidar R, Rosenberg M, Ambrogio L, Auclair D, Wang J, Song YK, et al. Comprehensive genomic analysis of rhabdomyosarcoma reveals a landscape of alterations affecting a common genetic axis in fusion-positive and fusion-negative tumors. Cancer Discov. 2014;4:216–231. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-13-0639. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Felix CA, Kappel CC, Mitsudomi T, Nau MM, Tsokos M, Crouch GD, Nisen PD, Winick NJ, Helman LJ. Frequency and diversity of p53 mutations in childhood rhabdomyosarcoma. Cancer Res. 1992;52:2243–2247. - PubMed
-
- McCubrey JA, Steelman LS, Abrams SL, Lee JT, Chang F, Bertrand FE, Navolanic PM, Terrian DM, Franklin RA, D'Assoro AB, et al. Roles of the RAF/MEK/ERK and PI3K/PTEN/AKT pathways in malignant transformation and drug resistance. Adv Enzyme Regul. 2006;46:249–279. doi: 10.1016/j.advenzreg.2006.01.004. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

