Modelling the response to vaccine in non-human primates to define SARS-CoV-2 mechanistic correlates of protection
- PMID: 35801637
- PMCID: PMC9282856
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.75427
Modelling the response to vaccine in non-human primates to define SARS-CoV-2 mechanistic correlates of protection
Abstract
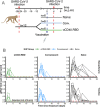
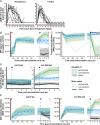
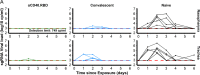
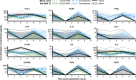
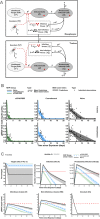
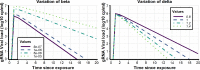
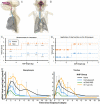
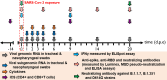
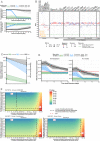
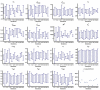
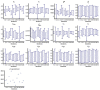
The definition of correlates of protection is critical for the development of next-generation SARS-CoV-2 vaccine platforms. Here, we propose a model-based approach for identifying mechanistic correlates of protection based on mathematical modelling of viral dynamics and data mining of immunological markers. The application to three different studies in non-human primates evaluating SARS-CoV-2 vaccines based on CD40-targeting, two-component spike nanoparticle and mRNA 1273 identifies and quantifies two main mechanisms that are a decrease of rate of cell infection and an increase in clearance of infected cells. Inhibition of RBD binding to ACE2 appears to be a robust mechanistic correlate of protection across the three vaccine platforms although not capturing the whole biological vaccine effect. The model shows that RBD/ACE2 binding inhibition represents a strong mechanism of protection which required significant reduction in blocking potency to effectively compromise the control of viral replication.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; correlate of protection; immunology; inflammation; neutralization; rhesus macaque; vaccines; viruses.
© 2022, Alexandre et al.
Conflict of interest statement
MA, RM, MP, SC, NK, SC, TN, BD, MS, MG, ND, MC, PM, MC, CL, AW, SZ, GZ, OS, RS, RL, YL, RT No competing interests declared
Figures






References
-
- Alter G, Yu J, Liu J, Chandrashekar A, Borducchi EN, Tostanoski LH, McMahan K, Jacob-Dolan C, Martinez DR, Chang A, Anioke T, Lifton M, Nkolola J, Stephenson KE, Atyeo C, Shin S, Fields P, Kaplan I, Robins H, Amanat F, Krammer F, Baric RS, Le Gars M, Sadoff J, de Groot AM, Heerwegh D, Struyf F, Douoguih M, van Hoof J, Schuitemaker H, Barouch DH. Immunogenicity of Ad26.COV2.S vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 variants in humans. Nature. 2021;596:268–272. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03681-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Asgharian B, Price O, McClellan G, Corley R, Einstein DR, Jacob RE, Harkema J, Carey SA, Schelegle E, Hyde D, Kimbell JS, Miller FJ. Development of a rhesus monkey lung geometry model and application to particle deposition in comparison to humans. Inhalation Toxicology. 2012;24:869–899. doi: 10.3109/08958378.2012.725782. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Balelli I, Pasin C, Prague M, Crauste F, Effelterre TV, Bockstal V, Solforosi L, Thiébaut R. A model for establishment, maintenance and reactivation of the immune response after vaccination against Ebola virus. Journal of Theoretical Biology. 2020;495:110254. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2020.110254. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

