Imaging-associated stress causes divergent phase transitions of RNA-binding proteins in the Caenorhabditis elegans germ line
- PMID: 35801939
- PMCID: PMC9434235
- DOI: 10.1093/g3journal/jkac172
Imaging-associated stress causes divergent phase transitions of RNA-binding proteins in the Caenorhabditis elegans germ line
Abstract
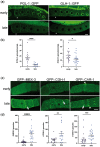
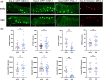
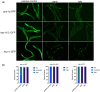
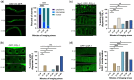
One emerging paradigm of cellular organization of RNA and RNA-binding proteins is the formation of membraneless organelles. Examples of membraneless organelles include several types of ribonucleoprotein granules that form via phase separation. A variety of intracellular pH changes and posttranslational modifications, as well as extracellular stresses, can stimulate the condensation of proteins into granules. For example, the assembly of stress granules induced by oxidative stress, osmotic stress, and heat stress has been well characterized in a variety of somatic cell types. In the germ line, similar stress-induced condensation of proteins occurs; however, less is known about the role of phase separation during gamete production. Researchers who study phase transitions often make use of fluorescent reporters to study the dynamics of RNA-binding proteins during live cell imaging. In this report, we demonstrate that common conditions of live-imaging Caenorhabditis elegans can cause an inadvertent stress and trigger phase transitions of RNA-binding proteins. We show that this imaging-associated stress stimulates decondensation of multiple germ granule proteins and condensation of several P-body proteins. Proteins within larger ribonucleoprotein granules in meiotically arrested oocytes do not appear to be as sensitive to the stress as proteins in diakinesis oocytes of young hermaphrodites, with the exception of the germ granule protein PGL-1. Our results have important methodological implications for all researchers using live-cell imaging techniques. The data also suggest that the RNA-binding proteins within large ribonucleoprotein granules of arrested oocytes may have distinct phases, which we characterize in our companion article.
Keywords: RNA-binding protein; RNP granule; condensation; live imaging; oogenesis; phase transition; stress.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Genetics Society of America.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Large RNP granules in Caenorhabditis elegans oocytes have distinct phases of RNA-binding proteins.G3 (Bethesda). 2022 Aug 25;12(9):jkac173. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkac173. G3 (Bethesda). 2022. PMID: 35816006 Free PMC article.
-
RNAi Screen Identifies Novel Regulators of RNP Granules in the Caenorhabditis elegans Germ Line.G3 (Bethesda). 2016 Aug 9;6(8):2643-54. doi: 10.1534/g3.116.031559. G3 (Bethesda). 2016. PMID: 27317775 Free PMC article.
-
Biphasic adaptation to osmotic stress in the C. elegans germ line.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2017 Jun 1;312(6):C741-C748. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00364.2016. Epub 2017 Apr 5. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28381521 Free PMC article.
-
Membraneless organelles: P granules in Caenorhabditis elegans.Traffic. 2019 Jun;20(6):373-379. doi: 10.1111/tra.12644. Epub 2019 Apr 11. Traffic. 2019. PMID: 30924287 Free PMC article. Review.
-
P granule assembly and function in Caenorhabditis elegans germ cells.J Androl. 2010 Jan-Feb;31(1):53-60. doi: 10.2164/jandrol.109.008292. Epub 2009 Oct 29. J Androl. 2010. PMID: 19875490 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Large RNP granules in Caenorhabditis elegans oocytes have distinct phases of RNA-binding proteins.G3 (Bethesda). 2022 Aug 25;12(9):jkac173. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkac173. G3 (Bethesda). 2022. PMID: 35816006 Free PMC article.
-
C. elegans germ granules sculpt both germline and somatic RNAome.Nat Commun. 2023 Sep 25;14(1):5965. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-41556-4. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37749091 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleoporin foci are stress-sensitive condensates dispensable for C. elegans nuclear pore assembly.EMBO J. 2023 Jul 3;42(13):e112987. doi: 10.15252/embj.2022112987. Epub 2023 May 31. EMBO J. 2023. PMID: 37254647 Free PMC article.
-
FG repeats drive co-clustering of nuclear pores and P granules in the C. elegans germline.Development. 2025 Mar 15;152(6):dev204585. doi: 10.1242/dev.204585. Epub 2025 Mar 27. Development. 2025. PMID: 40067309 Free PMC article.
-
The CCT chaperonin and actin modulate the ER and RNA-binding protein condensation during oogenesis and maintain translational repression of maternal mRNA and oocyte quality.Mol Biol Cell. 2024 Oct 1;35(10):ar131. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E24-05-0216. Epub 2024 Aug 21. Mol Biol Cell. 2024. PMID: 39167497 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alberti S, Carra S.. Quality control of membraneless organelles. J Mol Biol. 2018;430(23):4711–4729. - PubMed
-
- Boag PR, Nakamura A, Blackwell TK.. A conserved RNA-protein complex component involved in physiological germline apoptosis regulation in C. elegans. Development. 2005;132(22):4975–4986. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
