PIM2 Expression Induced by Proinflammatory Macrophages Suppresses Immunotherapy Efficacy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- PMID: 35802648
- PMCID: PMC9478531
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-21-3899
PIM2 Expression Induced by Proinflammatory Macrophages Suppresses Immunotherapy Efficacy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
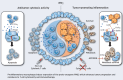
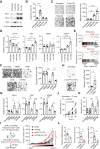
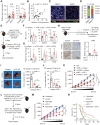
Cancer immunotherapy restores or enhances the effector function of T cells in the tumor microenvironment, but the efficacy of immunotherapy has been hindered by therapeutic resistance. Here, we identify the proto-oncogene serine/threonine protein kinase PIM2 as a novel negative feedback regulator of IFNγ-elicited tumor inflammation, thus endowing cancer cells with aggressive features. Mechanistically, IL1β derived from IFNγ-polarized tumor macrophages triggered PIM2 expression in cancer cells via the p38 MAPK/Erk and NF-κB signaling pathways. PIM2+ cancer cells generated by proinflammatory macrophages acquired the capability to survive, metastasize, and resist T-cell cytotoxicity and immunotherapy. A therapeutic strategy combining immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) with IL1β blockade or PIM2 kinase inhibition in vivo effectively and successfully elicited tumor regression. These results provide insight into the regulatory and functional features of PIM2+ tumors and suggest that strategies to influence the functional activities of inflammatory cells or PIM2 kinase may improve the efficacy of immunotherapy.
Significance: Cross-talk between T cells and macrophages regulates cancer cell PIM2 expression to promote cancer aggressiveness, revealing translational approaches to improve response to ICB in hepatocellular carcinoma.
©2022 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures




References
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 2011;144:646–74. - PubMed
-
- Maman S, Witz IP. A history of exploring cancer in context. Nat Rev Cancer 2018;18:359–76. - PubMed
-
- Hou J, Zhang H, Sun B, Karin M. The immunobiology of hepatocellular carcinoma in humans and mice: basic concepts and therapeutic implications. J Hepatol 2020;72:167–82. - PubMed
-
- Craig AJ, von Felden J, Garcia-Lezana T, Sarcognato S, Villanueva A. Tumor evolution in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2020;17:139–52. - PubMed
-
- Kuang DM, Zhao Q, Wu Y, Peng C, Wang J, Xu Z, et al. Peritumoral neutrophils link inflammatory response to disease progression by fostering angiogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 2011;54:948–55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

