Efficacy and safety of a single dose of casirivimab and imdevimab for the prevention of COVID-19 over an 8-month period: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial
- PMID: 35803290
- PMCID: PMC9255947
- DOI: 10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00416-9
Efficacy and safety of a single dose of casirivimab and imdevimab for the prevention of COVID-19 over an 8-month period: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial
Erratum in
-
Correction to Lancet Infect Dis 2022; published online July 5. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00416-9.Lancet Infect Dis. 2022 Sep;22(9):e239. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00501-1. Epub 2022 Jul 15. Lancet Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 35850126 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: There is an unmet need for COVID-19 prevention in patient populations who have not mounted or are not expected to mount an adequate immune response to complete COVID-19 vaccination. We previously reported that a single subcutaneous 1200 mg dose of the monoclonal antibody combination casirivimab and imdevimab (CAS + IMD) prevented symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infections by 81·4% in generally healthy household contacts of SARS-CoV-2-infected individuals over a 1-month efficacy assessment period. Here we present additional results, including the 7-month follow-up period (months 2-8), providing additional insights about the potential for efficacy in pre-exposure prophylaxis settings.
Methods: This was a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial done in the USA, Romania, and Moldova in 2020-2021, before the emergence of omicron (B.1.1.529) and omicron-lineage variants. Uninfected and unvaccinated household contacts of infected individuals, judged by the investigator to be in good health, were randomly assigned (1:1) to receive 1200 mg CAS + IMD or placebo by subcutaneous injection according to a central randomisation scheme provided by an interactive web response system; randomisation was stratified per site by the test results of a local diagnostic assay for SARS-CoV-2 and age group at baseline. COVID-19 vaccines were prohibited before randomisation, but participants were allowed to receive COVID-19 vaccination during the follow-up period. Participants who developed COVID-19 symptoms during the follow-up period underwent RT-PCR testing. Prespecified endpoints included the proportion of previously uninfected and baseline-seronegative participants (seronegative-modified full analysis set) who had RT-PCR-confirmed COVID-19 in the follow-up period (post-hoc for the timepoints of months 2-5 and 6-8 only) and underwent seroconversion (ie, became seropositive, considered a proxy for any SARS-CoV-2 infections [symptomatic and asymptomatic]; prespecified up to day 57, post-hoc for all timepoints thereafter). We also assessed the incidence of treatment-emergent adverse events. This study is registered with ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT04452318.
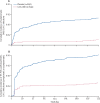
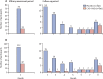
Findings: From July 13, 2020, to Oct 4, 2021, 2317 participants who were RT-PCR-negative for SARS-CoV-2 were randomly assigned, of whom 1683 (841 assigned to CAS + IMD and 842 assigned to placebo) were seronegative at baseline. During the entirety of the 8-month study, CAS + IMD reduced the risk of COVID-19 by 81·2% (nominal p<0·0001) versus placebo (prespecified analysis). During the 7-month follow-up period, protection was greatest during months 2-5, with a 100% relative risk reduction in COVID-19 (nominal p<0·0001; post-hoc analysis). Efficacy waned during months 6-8 (post-hoc analysis). Seroconversion occurred in 38 (4·5%) of 841 participants in the CAS + IMD group and in 181 (21·5%) of 842 in the placebo group during the 8-month study (79·0% relative risk reduction vs placebo; nominal p<0·0001). Six participants in the placebo group were hospitalised due to COVID-19 versus none who received CAS + IMD. Serious treatment-emergent adverse events (including COVID-19) were reported in 24 (1·7%) of 1439 participants receiving CAS + IMD and in 23 (1·6%) of 1428 receiving placebo. Five deaths were reported, none of which were due to COVID-19 or related to the study drugs.
Interpretation: CAS + IMD is not authorised in any US region as of Jan 24, 2022, because data show that CAS + IMD is not active against omicron-lineage variants. In this study, done before the emergence of omicron-lineage variants, a single subcutaneous 1200 mg dose of CAS + IMD protected against COVID-19 for up to 5 months of community exposure to susceptible strains of SARS-CoV-2 in the pre-exposure prophylaxis setting, in addition to the post-exposure prophylaxis setting that was previously shown.
Funding: Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, F Hoffmann-La Roche, US National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, US National Institutes of Health.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests GAH, MPO, FI, KCT, and JDH are Regeneron Pharmaceuticals employees and stockholders who report having a patent pending (International Patent application number PCT/US2021/035556), which has been licensed and provides royalties, with Regeneron Pharmaceuticals. EF-N, NSa, PH, K-CC, BJM, JDD, AM, JP, DS, ATD, NB, and DMW are Regeneron Pharmaceuticals employees and stockholders. MSC reports a relationship with National Institute for Health for study funding and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals for drug studies and manuscript writing support, and has a leadership or fiduciary role for HIV Prevention Trials Network, COVID-29 Prevention Network, Fogart, and McGill. CBH reports support for manuscript writing from Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, salary support from University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, activities sponsored by Gilead Sciences, and receiving honorarium for developing content for a continuing education programme with PRIME Education. MAM reports being a federal employee who, as part of the US Government through Operation Warp Speed (later transferred into the responsibilities of the White House COVID-19 Response Team), supported the clinical trial network involved in implementation of this effort. ATH is a Regeneron Pharmaceuticals employee and stockholder, a former Pfizer employee and current stockholder, and reports having a patent pending (International Patent application number PCT/US2021/035556), which has been licensed and provides royalties, with Regeneron Pharmaceuticals. AB, CAK, NSt, and GDY have issued patents (US patent number 10 787 501, 10 954 289, and 10 975 139) and pending patents (International Patent application number PCT/US2020/039707), which have been licensed and provide royalties, with Regeneron Pharmaceuticals. KJB and DRB declare no competing interests.
Figures
Comment in
-
Stewardship of COVID-19 volunteers by nested trial design.Lancet Infect Dis. 2022 Oct;22(10):1400-1401. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00429-7. Epub 2022 Jul 5. Lancet Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 35803288 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- WHO WHO Director-General's opening remarks at the media briefing on COVID-19—11 March 2020. 2020. https://www.who.int/director-general/speeches/detail/who-director-genera...
-
- Telenti A, Arvin A, Corey L, et al. After the pandemic: perspectives on the future trajectory of COVID-19. Nature. 2021;596:495–504. - PubMed
-
- COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines Panel . National Institutes of Health; 2021. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) treatment guidelines.https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/ - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

