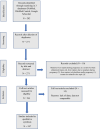
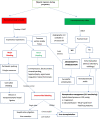
Hypertensive disorders in pregnancy complicated by liver rupture or hematoma: a systematic review of 391 reported cases
- PMID: 35804368
- PMCID: PMC9270816
- DOI: 10.1186/s13017-022-00444-w
Hypertensive disorders in pregnancy complicated by liver rupture or hematoma: a systematic review of 391 reported cases
Abstract
Background: Spontaneous liver rupture in pregnancy is often unrecognized, highly lethal, and not completely understood. The goal was to summarize and define the etiology, risk factors, clinical presentation, appropriate diagnostic methods, and therapeutic options for spontaneous hepatic rupture during pregnancy/puerperium (SHRP) complicated by the hypertensive disorder.
Methods: Literature search of all full-text articles included PubMed (1946-2021), PubMed Central (1900-2021), and Google Scholar. Case reports of a spontaneous hepatic rupture or liver hematoma during pregnancy or puerperium as a complication of hypertensive disorders (preeclampsia, eclampsia, HELLP syndrome) were searched. There was no restriction of language to collect the cases. Additional cases were identified by reviewing references of retrieved studies. PRISMA guidelines for the data extraction and quality assessment were applied.
Results: Three hundred and ninety-one cases were collected. The median maternal age was 31 (range 17-48) years; 36.6% were nulliparous. Most (83.4%) occurred in the third trimester. Maternal and fetal mortality was 22.1% and 37.2%, respectively. Maternal and fetal mortality was significantly higher 1) before the year 1990, 2) with maternal hemodynamic instability, and 3) eclampsia. The most important risk factors for SHRP were preeclampsia and HELLP syndrome. Most women had right lobe affected (70.9%), followed by both lobes in 22.1% and left lobe in 6.9%. The most common surgical procedure was liver packing. Liver transplantation was performed in 4.7% with 100% survival. Maternal mortality with liver embolization was 3.0%. Higher gestational age increases fetal survival.
Conclusion: The diagnosis and treatment of SHRP are often delayed, leading to high maternal and fetal mortality. SHRP should be excluded in hemodynamically unstable patients with preeclampsia/eclampsia or HELLP syndrome and right upper abdominal pain. Liver embolization and liver transplantation contribute to maternal survival. Maternal and fetal mortality was significantly higher before the year 1990. Hemodynamic instability, preeclampsia, and eclampsia have a significant negative influence on maternal survival.
Level of evidence: Level V.
Keywords: Cesarean delivery; Eclampsia; Fetal death; HELLP syndrome; Liver hematoma; Liver rupture; Preeclampsia; Pregnancy; Puerperium; Treatment.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Abercrombie J. Hemorrhage of the liver. L Med Gaz. 1844;34:92–5.
-
- Viswanathan M, Ansari M, Berkman N, Chang S, Hartling L, McPheeters, LM Santaguida P, et al. Assessing the Risk of Bias of Individual Studies in Systematic Reviews of Health Care Interventions. Assess Risk Bias Individ Stud Syst Rev Heal Care Interv. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality Methods Guide for Comparative Effectiveness Review; 2012.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials