Screening of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum with High Stress Tolerance and High Esterase Activity and Their Effect on Promoting Protein Metabolism and Flavor Formation in Suanzhayu, a Chinese Fermented Fish
- PMID: 35804748
- PMCID: PMC9265898
- DOI: 10.3390/foods11131932
Screening of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum with High Stress Tolerance and High Esterase Activity and Their Effect on Promoting Protein Metabolism and Flavor Formation in Suanzhayu, a Chinese Fermented Fish
Abstract
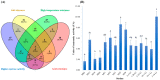
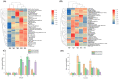
In this study, three Lactiplantibacillus plantarum, namely 3-14-LJ, M22, and MB1, with high acetate esterase activity, acid, salt, and high-temperature tolerance were selected from 708 strains isolated from fermented food. Then, L. plantarum strains MB1, M22, and 3-14-LJ were inoculated at 107 CFU/mL in the model and 107 CFU/g in actual Suanzhayu systems, and the effects during fermentation on the physicochemical properties, amino acid, and volatile substance were investigated. The results showed that the inoculated group had a faster pH decrease, lower protein content, higher TCA-soluble peptides, and total amino acid contents than the control group in both systems (p < 0.05). Inoculation was also found to increase the production of volatile compounds, particularly esters, improve the sour taste, and decrease the bitterness of the product (p < 0.05). L. plantarum M22 was more effective than the other two strains in stimulating the production of isoamyl acetate, ethyl hexanoate, and ethyl octanoate. However, differences were discovered between the strains as well as between the model and the actual systems. Overall, the isolated strains, particularly L. plantarum M22, have good fermentation characteristics and have the potential to become excellent Suanzhayu fermenters in the future.
Keywords: Lactiplantibacillus plantarum; esters; fermented fish; protein metabolism; starter culture; volatile compounds.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ho V.T.T., Lo R., Bansal N., Turner M.S. Characterisation of Lactococcus lactis isolates from herbs, fruits and vegetables for use as biopreservatives against Listeria monocytogenes in cheese. Food Control. 2018;85:472–483. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2017.09.036. - DOI
-
- Wah T.T., Walaisri S., Assavanig A., Niamsiri N., Lertsiri S. Co-culturing of Pichia guilliermondii enhanced volatile flavor compound formation by Zygosaccharomyces rouxii in the model system of Thai soy sauce fermentation. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013;160:282–289. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2012.10.022. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Visessanguan W., Benjakul S., Smitinont T., Kittikun C., Thepkasikul P., Panya A. Changes in microbiological, biochemical and physico-chemical properties of Nham inoculated with different inoculum levels of Lactobacillus curvatus. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2006;39:814–826. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2005.05.006. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

